Conjugation is the single most crucial thing when it comes to verbs. Since these types of words change depending on the tense, mood, and person, you must get familiar with the rules for conjugating verbs in Spanish. So, in this, we’ll go over:
- What are Verb Conjugations?
- Steps to Conjugate Verbs
- When & When Not to Conjugate Spanish Verbs
- Key Points
- Spanish Verb Conjugation Related Resources
By the end of it, you’ll know the essentials of how to conjugate Spanish verbs. To make things easier, I’ve included different examples with basic verbs in Spanish.
Take Note: Spanish verbs are the part of speech that expresses the action (Yo leo) or describe the state of being of something (La casa es azul).
What Does Spanish Conjugation & Conjugating Verbs Mean?
Conjugating involves changing a verb’s ending to agree with the subject, mood, and tense. Simply put, when we conjugate a verb in Spanish, we change its ending to express:
- Who is doing the action (subject)
- When the action is done (tense)
- How is the action perceived (mood)
Take bailar as an example:
Yo bailo muy bien.
I dance very well.
Ellas bailaron en la fiesta.
They danced at the party.
Let’s focus on example #2. In this sentence, the Spanish conjugation communicates that they performed the action at some point in the past. Finally, the verb ending also indicates that this action is a fact (indicative mood).

As you can see, a verb’s conjugations provide a lot of information crucial for communicating. In the sections below, you’ll learn more about conjugating verbs in Spanish.
Take Note: In Spanish, nouns and adjectives are modified to express number and gender. This is called agreement in Spanish grammar. Verbs are also subject to agreement. However, verb agreement doesn’t focus on gender but rather on number –él vs ellos, tú vs ustedes, etc.
How to Conjugate Verbs in Spanish
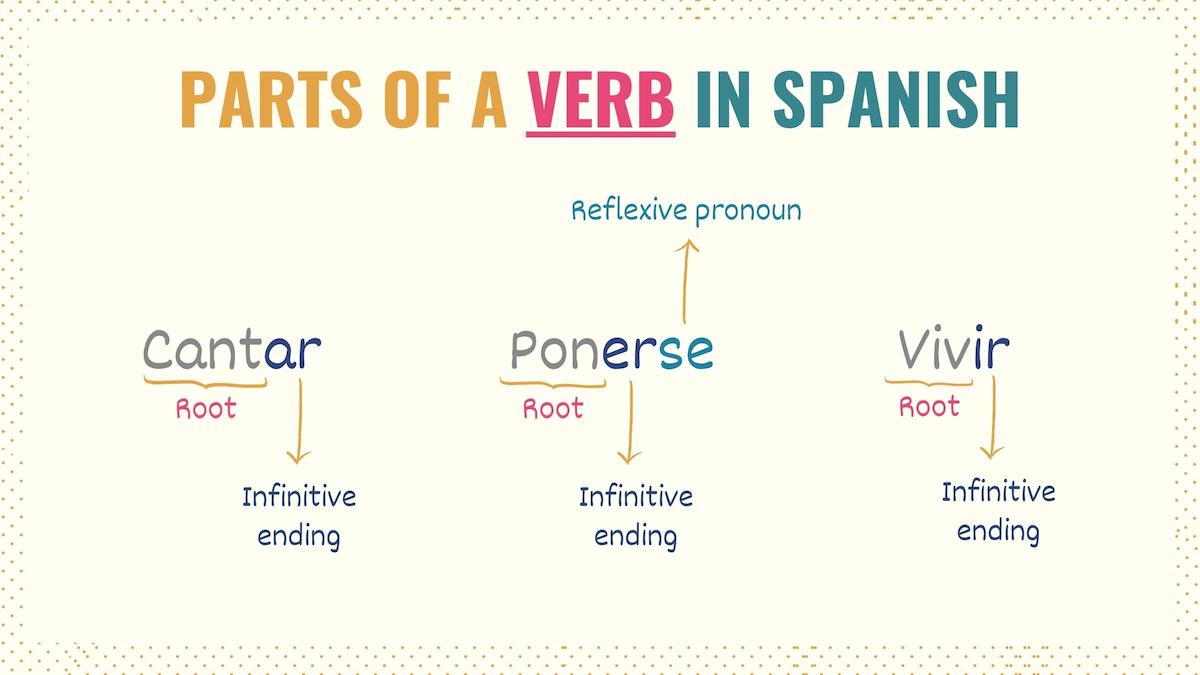
As established before, infinitive verbs in Spanish are verbs in their non-conjugated base form. Infinitives are recognized by three endings:
And why should you care about this? Because these infinitive endings are not only attached to the verb’s root but they also tell you the conjugation model (more commonly called conjugation type in English) you must follow.
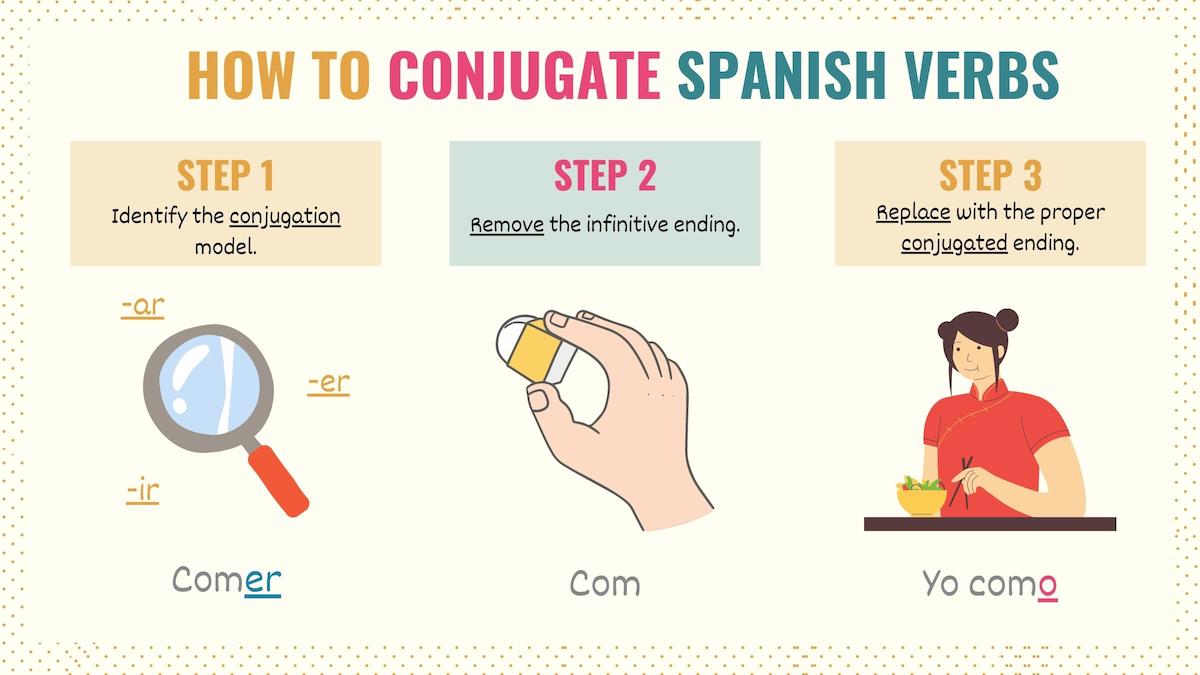
Once you understand this, the steps to conjugate a verb in Spanish are simple:
- Identify the conjugation type.
- Drop the infinitive ending to get the verb’s root.
- Replace it with the corresponding conjugation ending.
Remember that, unlike English, Spanish conjugation has different endings for all subject pronouns and tenses. In other words, when choosing an ending to conjugate a verb, you must ensure it agrees with the person.
Regular Verbs vs Stem-Changing vs Irregular Verbs
Check this conjugation chart with buscar, aprender, and preferir:
| -AR | -ER | -IR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yo | Busco | Aprendo | Prefiero |
| Tú | Buscas | Aprendes | Prefieres |
| Él / EllaUsted | Busca | Aprende | Prefiere |
| Nosotros | Buscamos | Aprendemos | Preferimos |
| Vosotros | Buscáis | Aprendéis | Preferís |
| Ellos / EllasUstedes | Buscan | Aprenden | Prefieren |
As you can see in the table above, there are different types of verbs in Spanish. Regular verbs do not have any changes on their root (like aprender). On the other hand, the root of stem-changing verbs has minor spelling changes (like preferir).
On the other hand, a Spanish irregular verb (such as ir) changes its root and, in many cases, you must also use different endings.
Conjugating reflexive verbs in Spanish
In Spanish, conjugating a reflexive verb is no different from how we conjugate other verbs. The only difference is that reflexives have the reflexive pronoun se in their infinitive form.
- Bañarse
- Ponerse
- Vestirse
This reflexive pronoun is subject to agreement. In other words, you must change it to agree with the subject. But, as you can see in the examples above, these verbs also have the -AR, -ER, and -IR terminations that tell you the conjugation pattern to follow.
For instance:
Yo me baño.
I shower.
Tú te bañas.
You shower.
Nosotros nos bañamos.
We shower.
Take Note: Unlike English, in Spanish, subject pronouns can be omitted because a conjugated verb already conveys who performs the action.
When & When Not to Conjugate Spanish Verbs
In Spanish, sentences with a single verb must be conjugated:
| Incorrect | Correct |
|---|---|
| Ella tener sueño. She to have sleepy. | Ella tiene sueño. She is sleepy. |
However, in sentences with an auxiliary verb, the auxiliary must be conjugated, and the second verb will remain in infinitive, present participle (aka gerund), or past participle form. For instance:
Van a comer.
They are going to eat.
¿Qué estás haciendo?
What are you doing?
No he visto esa película.
I have not seen that movie.
Key Points
Spanish conjugation is key for communicating effectively. Here are some key points you should keep in mind:
- Conjugated verbs express who performs the action, when it happens, and how factual (or hypothetical) that activity is.
- In Spanish, each subject has its own conjugation ending. Therefore, these pronouns can be omitted.
- Non-conjugated verbs ending with -AR, -ER, and -IR. These are different conjugation models.
- The root of a verb is attached to these endings.
- To conjugate in Spanish, you must remove the infinitive termination and add the proper ending to the verb’s root.
- The stem of regular verbs never changes.
- As its name suggests, the root of stem-changing verbs has minor spelling modifications.
- Irregular verbs have dramatic changes in their stem and, sometimes, in their terminations.
- The second verb in a sentence can be a gerund, past participle or infinitive.
Next Steps: Resources for Spanish Verbs & Conjugations
Here are some additional links you can check if you want to improve your command of Spanish verbs. As mentioned above, there are three different types of conjugation patterns. So, check these guides on how to conjugate -AR, -ER, and -IR verbs.
When you’re ready to put your skills to the test, you can check out the Spanish Verb Conjugator Hub. It’s a list of the most common Spanish verbs with conjugation guides in the critical verb tenses. Each verb also has its own quiz where you practice its conjugations. This is a great way to practice regular and irregular verbs.
In this guide to Spanish tenses, you’ll find a summary of different endings you need to conjugate a verb to different moments in time. Since a verb in Spanish must agree with the person doing the action, you should also review subject pronouns.
Although they follow the same rules you learned in this article, this guide focuses on conjugating reflexive verbs in Spanish. Check it to learn how to choose the correct pronoun and place it correctly in the sentence.
Download the Spanish Verb Conjugation PDF
Conjugating verbs is an essential part of learning to speak Spanish. Feel free to download a PDF copy on how to conjugate verbs in Spanish, which includes the key points and graphics for this guide. You’ll find the steps involved in conjugating verbs, the relationship between conjugations and tenses and more!



