Sentir is a common -IR verb with E to IE and E to I stem changes. Since this verb is not only common for your conversations but also to practice these patterns. In this guide, we’ll go over the sentir conjugation charts. Here is what you’ll learn:
- Sentir Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Sentir Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Sentir Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Sentir Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Sentir Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Sentir Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Sentir
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -IR |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Sentir |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Sintiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Sentido |
| Synonyms | Percibir, resentirse, lamentar. |
Stem Changes: E to IE and E to I
- Present Indicative: sient for all subject pronouns except ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’.
- Preterite: sint for ‘usted’, ‘él’, ‘ella’, and their plural forms.
- Present subjunctive: sient for ‘yo’, ‘tú’, and the third person singular and plural; sint for ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’.
- Imperfect subjunctive: sintie for all subject pronouns.
- Affirmative imperative: sient for all subjects except ‘vosotros’.
- Negative imperative: sient for ‘tú’, ‘usted’, ‘ustedes’; sint for ‘vosotros’.
Indicative Conjugations of Sentir
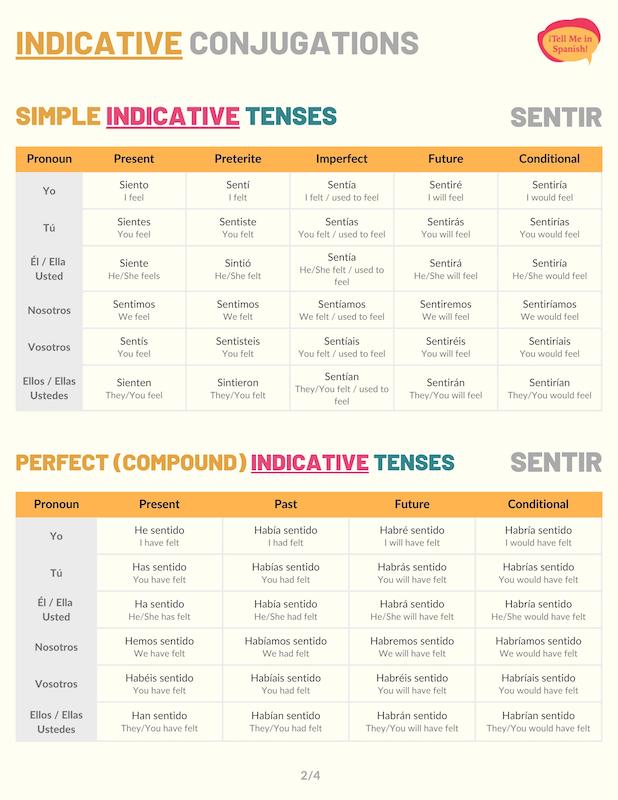
Present tense
Sentir present tense conjugations are formed with an E to IE stem change. However, ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’ don’t follow these changes. Use the present conjugations of sentir to talk about what or how people currently feel. For instance: ¿Cómo te sientes?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Siento | I feel |
| Tú | Sientes | You feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Siente | He/She feels You (formal) feel |
| Nosotros | Sentimos | We feel |
| Vosotros | Sentís | You feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sienten | They feel You (plural) feel |
Preterite tense
Sentir’s preterite conjugations have an E to I stem change only for the third person singular and plural. You can see this change in the sentir conjugation chart below. We use these preterite forms to communicate what or how a person felt in the past.
For example: ¿Sintieron el temblor?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sentí | I felt |
| Tú | Sentiste | You felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sintió | He/She felt You (formal) felt |
| Nosotros | Sentimos | We felt |
| Vosotros | Sentisteis | You felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sintieron | They felt You (plural) felt |
Imperfect tense
When conjugated to the imperfect indicative tense, sentir doesn’t have stem changes. Conjugate sentir to the imperfect tense to describe how people or things used to feel for an extended period of time in the past. For example: No nos sentíamos muy bien.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sentía | I felt I used to feel |
| Tú | Sentías | You felt You used to feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sentía | He/She felt He/She used to feel You (formal) felt You (formal) used to feel |
| Nosotros | Sentíamos | We felt We used to feel |
| Vosotros | Sentíais | You felt You used to feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sentían | They felt They used to feel You (plural) felt You (plural) used to feel |
Near future
The immediate or near future in Spanish is formed with the structure ir (present tense) + a + infinitive verb (sentir, in this case). Use these sentir conjugations to express what or how a person is about to feel. Here is a sentence: Pronto vas a sentirte mejor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a sentir | I’m going to feel |
| Tú | Vas a sentir | You’re going to feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a sentir | He/She is going to feel You (formal) are going to feel |
| Nosotros | Vamos a sentir | We’re going to feel |
| Vosotros | Vais a sentir | You’re going to feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a sentir | They’re going to feel You (plural) are going to feel |
Future simple tense
Conjugate sentir to the future tense in Spanish to express what people will feel or be sorry for at some point in the future. Si no le dices algo, lo sentirás toda la vida.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sentiré | I will feel |
| Tú | Sentirás | You will feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sentirá | He/She will feel You (formal) will feel |
| Nosotros | Sentiremos | We will feel |
| Vosotros | Sentiréis | You (formal) will feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sentirán | They will feel You (plural) will feel |
Conditional tense
Sentir conditional tense conjugation communicates what or how people would feel if an action was performed. You can also use these conjugations to guess how or what people would feel.
For instance: No te sentirías así si fueras a ver a un doctor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sentiría | I would feel |
| Tú | Sentirías | You would feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sentiría | He/She would feel You (formal) would feel |
| Nosotros | Sentiríamos | We would feel |
| Vosotros | Sentiríais | You would feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sentirían | They would feel You (plural) would feel |
Present perfect tense
To form the Spanish present perfect indicative tense, use the formula haber in the present tense + sentido (past participle). With these conjugations, sentir is used to talk about the things people have or haven’t felt. For instance: ¿Cómo se han sentido?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He sentido | I have felt |
| Tú | Has sentido | You have felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha sentido | He/She has felt You (formal) have felt |
| Nosotros | Hemos sentido | We have felt |
| Vosotros | Habéis sentido | You have felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han sentido | They have felt You (plural) have felt |
Past perfect
The past perfect in Spanish is formed with the imperfect form of ‘haber’ and the past participle form of ‘sentir’. Conjugate sentir to this tense to communicate that a person had or hadn’t felt someway before a past action or the moment of speaking.
For example: Nunca había sentido tanto frío.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había sentido | I had felt |
| Tú | Habías sentido | You had felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había sentido | He/She had felt You (formal) had felt |
| Nosotros | Habíamos sentido | We had felt |
| Vosotros | Habíais sentido | You had felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían sentido | They had felt You (plural) had felt |
Future perfect
Sentir future perfect conjugations refer to the things people will have felt or been sorry for by or before a certain moment in the future. You can also use these future forms to talk about what someone might have felt. Para el lunes, ya te habrás sentido mejor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré sentido | I will have felt |
| Tú | Habrás sentido | You will have felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá sentido | He/She will have felt You (formal) will have felt |
| Nosotros | Habremos sentido | We will have felt |
| Vosotros | Habréis sentido | You will have felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán sentido | They will have felt You (plural) will have felt |
Conditional perfect
We use the sentir conditional perfect conjugations to express what or how someone would have felt if a past condition had been met. For example: Si te hubieras puesto un suéter, no habrías sentido tanto frío.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría sentido | I would have felt |
| Tú | Habrías sentido | You would have felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría sentido | He/She would have felt You (formal) would have felt |
| Nosotros | Habríamos sentido | We would have felt |
| Vosotros | Habríais sentido | You would have felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían sentido | They would have felt You (plural) would have felt |
Progressive tenses
Sentir’s Spanish progressive forms allow you to convey how or what someone is feeling at the moment of speaking. These tenses are formed with estar + sintiendo (present participle). Here is an example: ¿Qué estás sintiendo?
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + sintiendo | I am feeling |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + sintiendo | You were feeling |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + sintiendo | He was feeling |
| Future | Estar (future) + sintiendo | We will be feeling |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + sintiendo | They would be feeling |
Take Note: Sentir has an E to I stem change when forming the present participle in Spanish. Like ‘sentir’, there are other verbs whose gerunds have a stem change. You can check the list here.
Sentir Subjunctive Conjugations
The subjunctive mood in Spanish communicates wishes, requests, suggestions, expectations, doubts, or hypothetical situations. Below are sentir conjugation charts for the most common subjunctive tenses. Notice that these tenses also have some stem changes.
Present subjunctive
The present subjunctive conjugations of sentir have two different stem changes. The first one is an E to IE change which applies to all pronouns except ‘vosotros’ and ‘nosotros’. For these pronouns, you’ll use an E to I stem change.
Sentir subjunctive conjugations allow you to express expectations, wishes, suggestions, or requests about the way people feel. For instance: No quiero que sientan dolor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sienta | I feel |
| Tú | Sientas | You feel |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sienta | He/She feels You (formal) feel |
| Nosotros | Sintamos | We feel |
| Vosotros | Sintáis | You feel |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sientan | They feel You (plural) feel |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber in the present subjunctive + sentido is the formula we use to build the present perfect subjunctive of ‘sentir’. We use these subjunctive conjugations to wonder or wish that a person has felt something or a certain way. For example: Ojalá no hayas sentido nada.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya sentido | I have felt |
| Tú | Hayas sentido | You have felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya sentido | He/She has felt You (formal) have felt |
| Nosotros | Hayamos sentido | We have felt |
| Vosotros | Hayáis sentido | You have felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan sentido | They have felt You (plural) have felt |
Imperfect subjunctive
Sentir’s imperfect subjunctive conjugations have an E to I stem change. In other words, you’ll use the stem sintie to form these conjugations. The imperfect forms of ‘sentir’ communicate past suggestions, requests, wishes someone had about the way someone felt.
For instance: No creí que sintieras tanto frío.
The imperfect subjunctive has two conjugation models depending on the type of Spanish you use:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sintiera | I felt |
| Tú | Sintieras | You felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sintiera | He/She felt You (formal) felt |
| Nosotros | Sintiéramos | We felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sintieran | They felt You (plural) felt |
Note: Vosotros is not used in Latin American Spanish. As a result, the conjugation for this pronoun hasn’t been included in the conjugation table above.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Sintiese | I felt |
| Tú | Sintieses | You felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Sintiese | He/She felt You (formal) felt |
| Nosotros | Sintiésemos | We felt |
| Vosotros | Sintieseis | You felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Sintiesen | They felt You (plural) felt |
Past perfect subjunctive
Conjugate sentir to the past perfect subjunctive to communicate how or what someone would have felt if a past circumstance was met. These conjugations can also convey regret for something you had or hadn’t felt.
For example: Si no hubieras estado dormido, es probable que hubieras sentido el temblor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera sentido | I had felt |
| Tú | Hubieras sentido | You had felt |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera sentido | He/She had felt You (formal) had felt |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos sentido | We had felt |
| Vosotros | Hubierais sentido | You had felt |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran sentido | They had felt You (plural) had felt |
Sentir Imperative Conjugations
The Spanish imperative mood allows you to give orders to people.
Affirmative commands
To form the affirmative commands of sentir, use the stem sient for all subjects but ‘vosotros’. Use these imperative forms to command people to feel something. For instance: Mira, ven y siente esto.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Siente | Feel |
| Usted | Sienta | Feel |
| Vosotros | Sentid | Feel |
| Ustedes | Sientan | Feel |
Negative commands
Similar to the present subjunctive conjugations, the negative imperative of sentir has two stem changes. The first one, an E to IE stem change, is applied to ‘tú’, ‘usted’, and ‘ustedes’. The second one is an E to I change, and it’s only applied to ‘vosotros’.
Use the negative imperative of ‘sentir’ to command people not to feel a certain way. No te sientas mal, todos cometemos errores.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No sientas | Don’t feel |
| Usted | No sienta | Don’t feel |
| Vosotros | No sintáis | Don’t feel |
| Ustedes | No sientan | Don’t feel |
Meanings of Sentir & Examples
Since you already know how to conjugate sentir in Spanish, here are some common applications and examples of this verb.
1. Express condolences, sorrow or regrets
[Sentir conjugated] + (adv) + [complement]
Siento mucho lo que te dije.
I am very sorry for what I said.
Sentimos mucho lo que te pasó.
We feel sorry about what happened to you.
2. Describe how people or things feel
(Reflexive pronoun) + [sentir conjugated] + [complement]
¿Se sienten mal?
Do you guys feel bad?
Claudia dijo que sentía un poco de dolor.
Claudia said that she felt a little bit of pain.
Take Note: Use Spanish reflexive pronouns to describe how a person is feeling. If you’re talking about how something you’re touching feels, you can use direct object pronouns to replace that thing.
Download Sentir Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
While sentir is not an irregular verb, it can be challenging to conjugate with its array of stem changes. So, I’ve created a downloadable PDF containing of the sentir conjugation charts, as well as the stem changes overview rules you can see at a glance as well as its definition and uses with examples.
Practice Quiz: Sentir Conjugation

Now that you know how to conjugate sentir in Spanish, you can take this sentir conjugation practice quiz to drill your knowledge of the different stem changes in the various tenses for this verb.





