Pagar conjugation patterns are essential to understand how verbs ending with -gar work. Additionally, this verb is frequently used in daily conversations. So, in this guide, you’ll learn how to conjugate pagar in Spanish.
- Pagar Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Pagar Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Pagar Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Pagar Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Pagar Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Pagar Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Pagar
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -AR |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Pagar |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Pagando |
| Past Participle Form | Pagado |
| Synonyms | Abonar, liquidar. |
Stem Changes: -gar to -gu
- Preterite: pagu only for ‘yo’.
- Present Subjunctive: pagu for all subject pronouns.
- Affirmative Imperative: pagu only for ‘usted’ and ‘ustedes’.
- Negative Imperative: pagu for all subject pronouns.
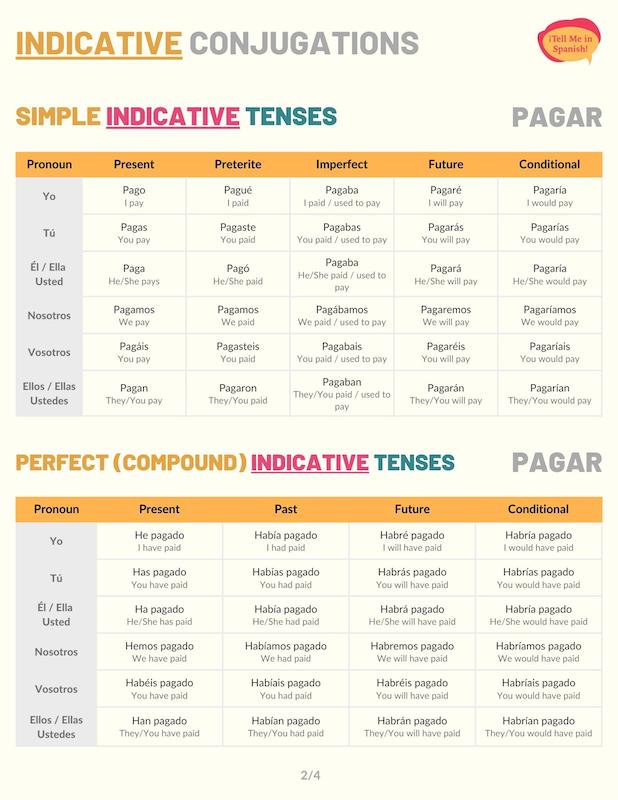
Indicative Conjugations of Pagar
Present tense
When conjugated to the present tense, this verbhas no stem changes. Use these conjugations of pagar to say that a person pays for something. For example: Vamos a los tacos, yo pago.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pago | I pay |
| Tú | Pagas | You pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Paga | He/She pays You (formal) pay |
| Nosotros | Pagamos | We pay |
| Vosotros | Pagáis | You pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagan | They pay You (plural) pay |
Preterite tense
Pagar preterite conjugations have a -gar to -gu change only for the pronoun ‘yo’. Use the preterite tense to explain that a person paid something at a specific moment in the past. For instance: ¿Ya le pagaste a Ellie?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagué | I paid |
| Tú | Pagaste | You paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagó | He/She paid You (formal) paid |
| Nosotros | Pagamos | We paid |
| Vosotros | Pagasteis | You paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagaron | They paid You (plural) paid |
Take Note: In Spanish, the letter g has a different pronunciation depending on the following vowel. The -gar to gu stem change is made to keep a soft g sound across all conjugations. Apply this rule to all verbs ending with –gar, such as jugar, llegar, apagar, etc.
Imperfect tense
Pagar conjugated to the Spanish imperfect tense expresses that people used to pay for something repeatedly in the past. For instance: Mi papá nos pagaba por limpiar la casa.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagaba | I paid I used to pay |
| Tú | Pagabas | You paid You used to pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagaba | He/She paid He/She used to pay You (formal) You (formal) used to pay |
| Nosotros | Pagábamos | We paid We used to pay |
| Vosotros | Pagabais | You paid You used to pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagaban | They paid They used to pay You (plural) paid You (plural) used to pay |
Near future
Use the present tense forms of ir + a + pagar (infinitive) to conjugate to the near future tense in Spanish. These pagar conjugations convey that someone will pay a person or for something in the immediate future. Here is an example: ¿Cuándo nos vas a pagar?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a pagar | I’m going to pay |
| Tú | Vas a pagar | You’re going to pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a pagar | He/She is going to pay You (formal) are going to pay |
| Nosotros | Vamos a pagar | We’re going to pay |
| Vosotros | Vais a pagar | You’re going to pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a pagar | They’re going to pay You (plural) are going to pay |
Future simple tense
The future simple conjugations of this verb convey that someone will pay another person or for something in the future. For instance: Si la rentamos, la casa se pagará sola.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagaré | I will pay |
| Tú | Pagarás | You will pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagará | He/She will pay You (formal) will pay |
| Nosotros | Pagaremos | We will pay |
| Vosotros | Pagaréis | You (formal) will pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagarán | They will pay You (plural) will pay |
Conditional tense
The pagar conditional conjugations convey that someone would pay. If applicable to your sentence, you can add conditions to express that a person would pay if a circumstance is met. For instance: ¿Sabes si Luis ya le pagaría a Esteban?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagaría | I would pay |
| Tú | Pagarías | You would pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagaría | He/She would pay You (formal) would pay |
| Nosotros | Pagaríamos | We would pay |
| Vosotros | Pagaríais | You would pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagarían | They would pay You (plural) would pay |
Present perfect tense
The Spanish present perfect is formed with haber present tense conjugations + pagado. Use these pagar conjugations to say whether someone has paid a person or for something. Here is a sentence: July ha pagado el internet los últimos tres meses.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He pagado | I have paid |
| Tú | Has pagado | You have paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha pagado | He/She has paid You (formal) have paid |
| Nosotros | Hemos pagado | We have paid |
| Vosotros | Habéis pagado | You have paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han pagado | They have paid You (plural) have paid |
Past perfect
Conjugate this verb to the Spanish past perfect tense to explain that a person had or hadn’t paid before another past action or moment. This tense is formed with haber (imperfect forms) + a + past participle verb (pagado for this example).
For instance: Discúlpenme, pensé que ya les había pagado.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había pagado | I had paid |
| Tú | Habías pagado | You had paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había pagado | He/She had paid You (formal) had paid |
| Nosotros | Habíamos pagado | We had paid |
| Vosotros | Habíais pagado | You had paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían pagado | They had paid You (plural) had paid |
Future perfect
If you want to express that someone will have paid for something by or before a certain future moment, you must conjugate this verb to the future perfect tense. For instance: En un año, habré pagado todas mis deudas.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré pagado | I will have paid |
| Tú | Habrás pagado | You will have paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá pagado | He/She will have paid You (formal) will have paid |
| Nosotros | Habremos pagado | We will have paid |
| Vosotros | Habréis pagado | You will have paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán pagado | They will have paid You (plural) will have paid |
Conditional perfect
In Spanish, the conditional perfect conjugations of pagar communicate that a person will have paid if a past condition had occurred. For example: Si no te hubiera dicho nada, estoy segura que no me habrías pagado.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría pagado | I would have paid |
| Tú | Habrías pagado | You would have paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría pagado | He/She would have paid You (formal) would have paid |
| Nosotros | Habríamos pagado | We would have paid |
| Vosotros | Habríais pagado | You would have paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían pagado | They would have paid You (plural) would have paid |
Progressive tenses
Use estar’s indicative conjugations + pagando (present participle) to form the progressive tenses in Spanish. These conjugations are used to convey that someone is paying at the moment of speaking. Here is an example: Tu papá está pagando la cuenta.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + pagando | I am paying |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + pagando | You were paying |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + pagando | He was paying |
| Future | Estar (future) + pagando | We will be paying |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + pagando | They would be paying |
Pagar Subjunctive Conjugations
The subjunctive mood in Spanish allows you to talk about expectations, hopes, demands, doubts, advice, hypothetical situations, or recommendations. The following pagar conjugation charts will show you how to conjugate this verb to the most common subjunctive tenses.
Present subjunctive
Pagar subjunctive conjugations have a -gar to gu change for all subject pronouns. These forms are used to suggest or hope that someone pays something. For example: Necesito que me pagues mañana.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pague | I pay |
| Tú | Pagues | You pay |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pague | He/She pays You (formal) pay |
| Nosotros | Paguemos | We pay |
| Vosotros | Paguéis | You pay |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Paguen | They pay You (plural) pay |
Take Note: When pronouncing the letter g in Spanish, the vowel e produces a hard g sound. However, in its infinitive form, pagar has a soft sound that we must keep across all conjugations. Since the present subjunctive endings start with ‘e’, we use the stem pagu to produce a soft g sound. This rule is applied to all verbs ending in -gar.
Present perfect subjunctive
In Spanish, the present perfect subjunctive tense is formed by using haber present subjunctive forms + pagado. These pagar conjugations allow you to communicate hopes or uncertainty about whether someone has paid something. Dudo que Juan ya le haya pagado a tu papá.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya pagado | I have paid |
| Tú | Hayas pagado | You have paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya pagado | He/She has paid You (formal) have paid |
| Nosotros | Hayamos pagado | We have paid |
| Vosotros | Hayáis pagado | You have paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan pagado | They have paid You (plural) have paid |
Imperfect subjunctive
The imperfect subjunctive tense is used to refer to past expectations, advice, suggestions, or requests you had about someone paying. Here is a sentence: Te pedí que me pagaras hoy.
Depending on the Spanish dialect you’re learning (Castilian or Latin American), there are two ways to conjugate the imperfect subjunctive in Spanish:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagara | I paid |
| Tú | Pagaras | You paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagara | He/She paid You (formal) paid |
| Nosotros | Pagáramos | We paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagaran | They paid You (plural) paid |
Note: Vosotros is not used in Latin American Spanish. As a result, this subject pronoun has been excluded from the previous pagar conjugation chart.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Pagase | I paid |
| Tú | Pagases | You paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Pagase | He/She paid You (formal) paid |
| Nosotros | Pagásemos | We paid |
| Vosotros | Pagaseis | You paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Pagasen | They paid You (plural) paid |
Past perfect subjunctive
Use the past perfect subjunctive of pagar to say that someone would have paid if a past circumstance took place. With these forms, you can also express regret for having paid something or not. Si hubiéramos pagado a tiempo, no habríamos acumulado tantos intereses.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera pagado | I had paid |
| Tú | Hubieras pagado | You had paid |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera pagado | He/She had paid You (formal) had paid |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos pagado | We had paid |
| Vosotros | Hubierais pagado | You had paid |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran pagado | They had paid You (plural) had paid |
Pagar Imperative Conjugations
In Spanish, the imperative conjugations are used to order people to do or not do something.
Affirmative commands
To maintain the pronunciation, use the stem pagu for ‘usted’ and ‘ustedes’. Pagar affirmative commands allow you to order someone to pay. For example: Págale a la señorita, por favor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Paga | Pay |
| Usted | Pague | Pay |
| Vosotros | Pagad | Pay |
| Ustedes | Paguen | Pay |
Negative commands
This verb’s negative command conjugations have an -gar to gu change. Use these imperative forms to order someone not to pay. No le pagues, ya no le debemos nada.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No pagues | Don’t pay |
| Usted | No pague | Don’t pay |
| Vosotros | No paguéis | Don’t pay |
| Ustedes | No paguen | Don’t pay |
Meanings of Pagar & Examples
Since now you know how to conjugate pagar, let’s check how you should use this verb. As the direct translation of ‘to pay’, this verb can refer to paying a person or for something:
[Pagar conjugated] + [complement]
Matt nunca paga a tiempo.
Matt never pays on time.
Espero que este año nos paguen mejor.
I hope they pay us better this year.
No tenemos internet, ¿sí lo pagaste?
We don’t have internet, did you pay for it?
Yo compré los boletos. Si los quieres, ¡págamelos!
I bought the tickets. If you want them, pay me.
Take Note: Pagar is a verb that takes both direct and indirect object pronouns. In this case, direct object pronouns replace the thing you pay, while indirect object pronouns refer to the person you’re paying to. As a result, this verb can work with Spanish double-object pronouns (example #4).
Download Pagar Conjugation Charts & Uses Cheat sheet
Pagar is one of the most common -AR verbs in Spanish as is critical for Spanish beginners to learn. It’s also a stem-changing verb in certain tenses, which can make it difficult to remember all its forms. I’ve created a cheat sheet PDF you can download containing all the pagar conjugation charts as well as examples of how to use this verb in daily conversations.
Practice Quiz: Pagar Conjugation

Now that you know how to conjugate one of the most important verbs in Spanish, the next step is to take the pagar conjugation practice quiz to master all of this verb’s different regular and stem-changing forms. You can choose any combination of tenses to include in the quiz, no matter your level of Spanish!





