Dormir is a basic -IR verb with O to UE stem changes. In some tenses, this verb also has an O to U change. Since this verb is essential for your communication and can help you practice these patterns, we’ll review the dormir conjugation rules in this guide.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- Dormir Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Dormir Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Dormir Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Dormir Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Dormir Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Dormir Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Dormir
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -IR |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Dormir |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Durmiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Dormido |
| Synonyms | Descansar, reposar, tomar una siesta. |
Stem Changes: O to UE and O to U.
- Present Indicative: duerm for all subject pronouns except ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’.
- Preterite: durm for the third-person singular and plural.
- Present Subjunctive: durm only for ‘nosotros’ and ‘vosotros’, duerm for the remaining pronouns.
- Imperfect Subjunctive: durmie for all subject pronouns.
- Affirmative Imperative: duerm for all subject pronouns except ‘vosotros’.
- Negative Imperative: durm only for ‘vosotros’, duerm for the remaining pronouns.
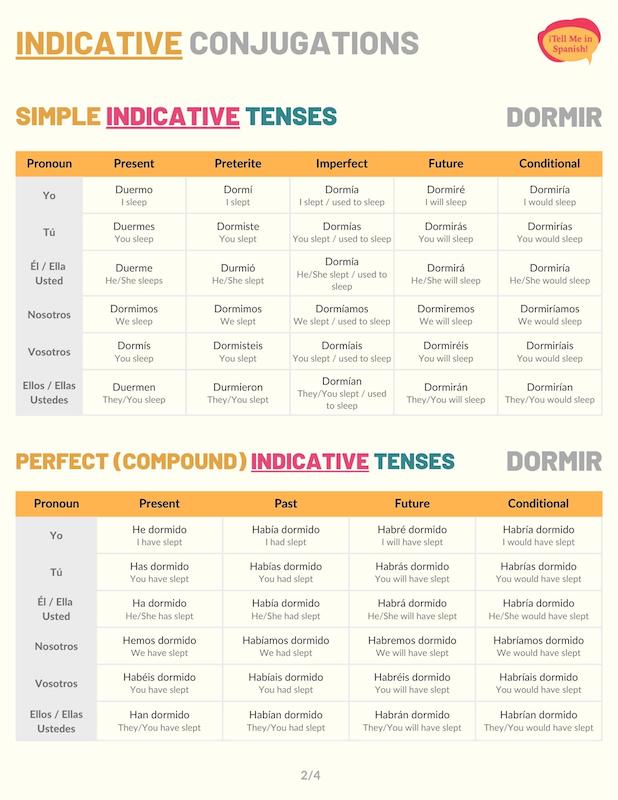
Indicative Conjugations of Dormir
Present tense
Dormir’s conjugations in the present tense have an O to UE stem change, which doesn’t affect the pronouns ‘vosotros’ and ‘nosotros’. See these changes in the dormir conjugation chart below. Use these forms to say that a person sleeps or describe how they do this activity.
For example: Los bebés duermen mucho.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Duermo | I sleep |
| Tú | Duermes | You sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Duerme | He/She sleeps You (formal) sleep |
| Nosotros | Dormimos | We sleep |
| Vosotros | Dormís | You sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Duermen | They sleep You (plural) sleep |
Preterite tense
Dormir preterite conjugations have an O to U stem change only for the third-person singular and plural. When conjugated to the preterite tense, dormir is used to say that a person slept. Add adverbs of time to mention the specific moment when this action happened.
Here is an example: ¿Durmieron bien?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Dormí | I slept |
| Tú | Dormiste | You slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Durmió | He/She slept You (formal) slept |
| Nosotros | Dormimos | We slept |
| Vosotros | Dormisteis | You slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Durmieron | They slept You (plural) slept |
Take Note: This O to U change is made to avoid having two ‘o’ sounds in a row and ease the pronunciation. So, dormó becomes durmió. This change is also applied to the verbs poder and morir.
Imperfect tense
In the past imperfect tense, this verb has no stem changes. Use dormir imperfect conjugations to describe how a person used to sleep. These forms are also used when it’s unclear when someone slept. For instance: Cuando eran niñas, mis primas dormían con la luz prendida.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Dormía | I slept I used to sleep |
| Tú | Dormías | You slept You used to sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Dormía | He/She slept He/She used to sleep You (formal) slept You (formal) used to sleep |
| Nosotros | Dormíamos | We slept We used to sleep |
| Vosotros | Dormíais | You slept You used to sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Dormían | They slept They used to sleep You (plural) slept You (plural) used to sleep |
Near future
In Spanish, the immediate future is conjugated by using ir (present tense) + a + dormir. We use these forms to say that someone will sleep soon. For example: Ya me voy a dormir.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a dormir | I’m going to sleep |
| Tú | Vas a dormir | You’re going to sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a dormir | He/She is going to sleep You (formal) are going to sleep |
| Nosotros | Vamos a dormir | We’re going to sleep |
| Vosotros | Vais a dormir | You’re going to sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a dormir | They’re going to sleep You (plural) are going to sleep |
Future simple tense
Conjugate dormir to the future simple tense to express that someone will sleep at some moment in the future. For example: En unos minutos, dormiré a la bebé.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Dormiré | I will sleep |
| Tú | Dormirás | You will sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Dormirá | He/She will sleep You (formal) will sleep |
| Nosotros | Dormiremos | We will sleep |
| Vosotros | Dormiréis | You (formal) will sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Dormirán | They will sleep You (plural) will sleep |
Conditional tense
In the conditional tense, dormir is used to say that a person would sleep. For instance: Si pudiéramos, nos dormiríamos más temprano.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Dormiría | I would sleep |
| Tú | Dormirías | You would sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Dormiría | He/She would sleep You (formal) would sleep |
| Nosotros | Dormiríamos | We would sleep |
| Vosotros | Dormiríais | You would sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Dormirían | They would sleep You (plural) would sleep |
Present perfect tense
The Spanish present perfect tense is formed with haber in the present form + dormido (past participle). These dormir conjugations allow you to express whether someone has slept or not. For instance: Esta semana, no he dormido muy bien.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He dormido | I have slept |
| Tú | Has dormido | You have slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha dormido | He/She has slept You (formal) have slept |
| Nosotros | Hemos dormido | We have slept |
| Vosotros | Habéis dormido | You have slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han dormido | They have slept You (plural) have slept |
Take Note: The past participle form of dormir (dormido) can also work as an adjective when combined with the verb estar. In this case, ‘dormido’ means ‘asleep’. El bebé está dormido.
Past perfect
Use dormir’s past perfect tense conjugations to say that someone had slept before a past action or moment. For example: Cuando llegó de trabajar, los niños ya se habían dormido.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había dormido | I had slept |
| Tú | Habías dormido | You had slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había dormido | He/She had slept You (formal) had slept |
| Nosotros | Habíamos dormido | We had slept |
| Vosotros | Habíais dormido | You had slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían dormido | They had slept You (plural) had slept |
Future perfect
When conjugated to the future perfect tense, this verb expresses that someone will have slept by or before a certain future moment or action. To form this tense, use haber future conjugations + the past participle form of ‘dormir’. For example: Al final de esta semana, sólo habré dormido 8 horas.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré dormido | I will have slept |
| Tú | Habrás dormido | You will have slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá dormido | He/She will have slept You (formal) will have slept |
| Nosotros | Habremos dormido | We will have slept |
| Vosotros | Habréis dormido | You will have slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán dormido | They will have slept You (plural) will have slept |
Conditional perfect
Conjugate this verb to the conditional perfect for conveying that someone would have slept if a past condition had occurred. Si mis vecinos le hubieran bajado a la música, habríamos dormido mejor.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría dormido | I would have slept |
| Tú | Habrías dormido | You would have slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría dormido | He/She would have slept You (formal) would have slept |
| Nosotros | Habríamos dormido | We would have slept |
| Vosotros | Habríais dormido | You would have slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían dormido | They would have slept You (plural) would have slept |
Progressive tenses
To form the progressive tenses in Spanish, use the estar conjugations + present participle (durmiendo, in this case). These dormir conjugations express that someone is sleeping at a given point in time.For example: No hagas ruido, mis papás están durmiendo.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + durmiendo | I am sleeping |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + durmiendo | You were sleeping |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + durmiendo | He was sleeping |
| Future | Estar (future) + durmiendo | We will be sleeping |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + durmiendo | They would be sleeping |
Take Note: Like dormir, there are other verbs whose present participle form in Spanish have stem changes.
Dormir Subjunctive Conjugations
The subjunctive mood in Spanish is used to refer to someone’s wishes, hopes, demands, advice, uncertainty, suggestions, or hypothetical situations. In the following sections, we’ll review dormir subjunctive conjugation charts.
Present subjunctive
Dormir subjunctive conjugations have an O to UE and O to U stem change. In the conjugations charts below, you can check which subject pronouns are affected by these patterns. Use these forms to talk about requests, suggestions, or wishes someone has about a person sleeping.
For instance: Les sugiero que duerman más.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Duerma | I sleep |
| Tú | Duermas | You sleep |
| Él / Ella Usted | Duerma | He/She sleeps You (formal) sleep |
| Nosotros | Durmamos | We sleep |
| Vosotros | Durmáis | You sleep |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Duerman | They sleep You (plural) sleep |
Present perfect subjunctive
In Spanish, the present perfect subjunctive of dormir is formed with haber subjunctive conjugations + past participle (dormido, for this conjugation guide). With this tense, dormir is used to wonder or wish that a person has already slept. Ojalá que la bebé ya se haya dormido.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya dormido | I have slept |
| Tú | Hayas dormido | You have slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya dormido | He/She has slept You (formal) have slept |
| Nosotros | Hayamos dormido | We have slept |
| Vosotros | Hayáis dormido | You have slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan dormido | They have slept You (plural) have slept |
Imperfect subjunctive
Durmie is the stem you must use to conjugate this verb to the imperfect subjunctive. These conjugations allow you to talk about past suggestions, requests or wishes someone had about a person’s sleep. For example: Te pedí que durmieras a los niños.
Based on the type of Spanish you’re learning (Latin American or Castilian), you must use a specific conjugation model for the imperfect subjunctive:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Durmiera | I slept |
| Tú | Durmieras | You slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Durmiera | He/She slept You (formal) slept |
| Nosotros | Durmiéramos | We slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Durmieran | They slept You (plural) slept |
Note: Latin American Spanish doesn’t use the pronoun vosotros. Because of that, this pronoun and its conjugation have not been included in the previous dormir conjugation chart.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Durmiese | I slept |
| Tú | Durmieses | You slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Durmiese | He/She slept You (formal) slept |
| Nosotros | Durmiésemos | We slept |
| Vosotros | Durmieseis | You slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Durmiesen | They slept You (plural) slept |
Past perfect subjunctive
The past perfect subjunctive conjugations of dormir express that someone would have slept if a past condition was met. These forms also express regret because you slept or not. For instance: Si no hubiera ido a esa fiesta, hubiera dormido más tiempo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera dormido | I had slept |
| Tú | Hubieras dormido | You had slept |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera dormido | He/She had slept You (formal) had slept |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos dormido | We had slept |
| Vosotros | Hubierais dormido | You had slept |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran dormido | They had slept You (plural) had slept |
Dormir Imperative Conjugations
In Spanish, we use the imperative conjugations of a verb to give orders.
Affirmative commands
Dormir affirmative commands have an O to UE stem change except for ‘vosotros’. Use these imperative forms to order someone to sleep or to wish someone a good night. Duerman bien.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Duerme | Sleep |
| Usted | Duerma | Sleep |
| Vosotros | Dormid | Sleep |
| Ustedes | Duerman | Sleep |
Negative commands
The negative commands of dormir are formed with two stems. Duerm for ‘tú’, ‘usted’, and ‘ustedes’, and durm for ‘vosotros’. You can use these conjugations to order someone not to sleep. No te duermas, ya casi llegamos.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No duermas | Don’t sleep |
| Usted | No duerma | Don’t sleep |
| Vosotros | No durmáis | Don’t sleep |
| Ustedes | No duerman | Don’t sleep |
Meanings of Dormir & Examples
So far, we’ve learned how to conjugate dormir in Spanish. Now, we’ll review some common applications of this verb. Based on the sentence and Spanish pronouns you use, dormir means to:
- Sleep or go to sleep
- Fall asleep (reflexive pronouns)
- Go numb (reflexive and indirect pronouns)
- Slack off or be careless
[Dormir conjugated] + [complement]
Los niños durmieron muy bien.
The kids slept very well.
A mi mamá se le durmió la pierna.
My mom’s leg went numb.
Te dormiste a la mitad de la película.
You fell asleep in the middle of the movie.
Si se duermen, el otro equipo les va a ganar.
If you slack off, the other team is going to win.
Take Note: The reflexive form dormirse follows the same conjugation pattern as ‘dormir’. You must only add the correct reflexive pronoun. Use dormir with adverbs of manner to describe how someone sleeps.
Download Dormir Conjugation Charts & Uses Cheat sheet
Dormir is a crucial Spanish -IR verb to know since it’s used in many conversations and to talk about daily routines. However, it’s also a stem-changing Spanish verb in many tenses. So, if you’d like a refresher on this verbs various forms, check out the dormir conjugation reference guide.
Practice Quiz: Dormir Conjugation

Practice this verb’s patterns by taking this dormir conjugation practice quiz. You can choose any combination of moods and tenses to include in the quiz, from beginner to advanced levels.





