Comprar is a common regular verb that can help you understand the conjugation pattern of -AR verbs. Since this is a necessary verb for daily life interactions, in this guide, you’ll learn the most important conjugations of comprar.
- Comprar Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Comprar Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Comprar Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Comprar Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Comprar Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Comprar Conjugation Practice Quiz
Take Note: There are many tenses in Spanish. However, we don’t use them all. Many are simply old and outdated. As a result, in this guide, you’ll only learn the tenses you need to know to become fluent in Spanish.
Overview of Comprar
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | ‘-AR’. |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Comprar |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Comprando |
| Past Participle Form | Comprado |
| Synonyms | Adquirir, obtener, sobornar. |
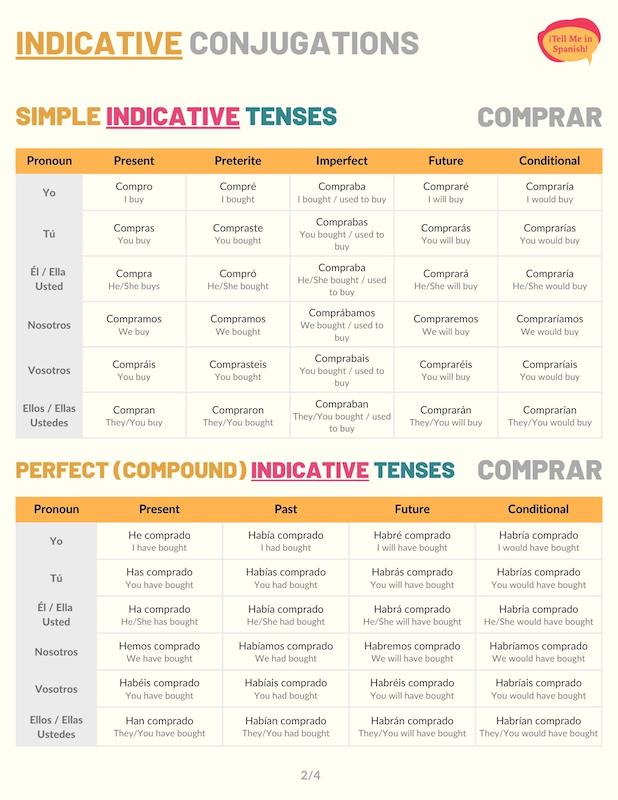
Indicative Conjugations of Comprar
Present tense
Comprar in the present tense refers to things you regularly buy or things you purchase in the present. For instance, aquí compro la verdura.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compro | I buy |
| Tú | Compras | You buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Compra | He/She buys You (formal) buy |
| Nosotros | Compramos | We buy |
| Vosotros | Compráis | You buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Compran | They buy You (plural) buy |
Preterite tense
The preterite form of comprar is used to talk about products or things someone bought at a specific moment in the past. Te compré estas flores.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compré | I bought |
| Tú | Compraste | You bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Compró | He/She bought You (formal) bought |
| Nosotros | Compramos | We bought |
| Vosotros | Comprasteis | You bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Compraron | They bought You (plural) bought |
Imperfect tense
The imperfect conjugation of comprar refers to things you used to buy or bought at some point in the past. For example, mis hermanos y yo comprábamos muchos dulces. Depending on the sentence, in the imperfect tense, ‘comprar’ can be translated as ‘used to buy’ or ‘bought’.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compraba | I bought I used to buy |
| Tú | Comprabas | You bought You use to buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Compraba | He/She bought He/She used to buy You (formal) You (formal) used to buy |
| Nosotros | Comprábamos | We bought We used to buy |
| Vosotros | Comprabais | You bought You used to buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Compraban | They bought They used to buy You (plural) bought You (plural) used to buy |
Near future
In the near future, comprar refers to things you currently plan to buy soon in the future. Mañana voy a comprar un reloj nuevo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a comprar | I’m going to buy |
| Tú | Vas a comprar | You’re going to buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a comprar | He/She is going to buy You (formal) are going to buy |
| Nosotros | Vamos a comprar | We’re going to buy |
| Vosotros | Vais a comprar | You’re going to buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a comprar | They’re going to buy You (plural) are going to buy |
Future simple tense
The future simple communicates that someone will buy a product or service at some point in the future. The future forms of comprar are all regular. For instance, algún día compraré ese coche.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compraré | I will buy |
| Tú | Comprarás | You will buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comprará | He/She will buy You (formal) will buy |
| Nosotros | Compraremos | We will buy |
| Vosotros | Compraréis | You (formal) will buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comprarán | They will buy You (plural) will buy |
Conditional tense
The conditional form of ‘comprar’ conveys that someone would buy something if certain circumstances are met. For example: si pudiera, compraría ese coche.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compraría | I would buy |
| Tú | Comprarías | You would buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Compraría | He/She would buy You (formal) would buy |
| Nosotros | Compraríamos | We would buy |
| Vosotros | Compraríais | You would buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comprarían | They would buy You (plural) would buy |
Present perfect tense
The present perfect conjugation of ‘comprar is formed with the verb ‘haber’ and comprado (the past participle form of ‘comprar’). The present perfect implies that you have or haven’t bought something in a moment close to the present. For instance, ¿no has comprado los boletos?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He comprado | I have bought |
| Tú | Has comprado | You have bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha comprado | He/She has bought You (formal) have bought |
| Nosotros | Hemos comprado | We have bought |
| Vosotros | Habéis comprado | You have bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han comprado | They have bought You (plural) have bought |
Past perfect
To conjugate the past perfect tense of ‘contar’, you need to use the imperfect form of haber + contado, which is the past participle form of ‘contar’. In this tense, ‘hablar’ can express that you bought something before some other reference point in the past. For example: pensé que ya habías comprado los boletos.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había comprado | I had bought |
| Tú | Habías comprado | You had bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había comprado | He/She had bought You (formal) had bought |
| Nosotros | Habíamos comprado | We had bought |
| Vosotros | Habíais comprado | You had bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían comprado | They had bought You (plural) had bought |
Future perfect
The future perfect of ‘comprar’ is built with the formula future form of haber + comprado. With this tense, ‘comprar’ expresses that someone will buy something by or before a certain time in the future. Creo que a esa hora ya habré comprado los boletos.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré comprado | I will have bought |
| Tú | Habrás comprado | You will have bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá comprado | He/She will have bought You (formal) will have bought |
| Nosotros | Habremos comprado | We will have bought |
| Vosotros | Habréis comprado | You will have bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán comprado | They will have bought You (plural) will have bought |
Conditional perfect
The conditional perfect of comprar refers to things you would have bought if a condition was met. For example, si hubiera sabido que venías, habría comprado más comida.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría comprado | I would have bought |
| Tú | Habrías comprado | You would have bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría comprado | He/She would have bought You (formal) would have bought |
| Nosotros | Habríamos comprado | We would have bought |
| Vosotros | Habríais comprado | You would have bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían comprado | They would have bought You (plural) would have bought |
Progressive tenses
Progressive tenses are used to talk about actions that are in progress at the moment of speaking. In other words, we use ‘comprar’ to express that someone is buying something right now. For instance, Cindy está comprando pollo. These tenses are formed with estar (conjugated) + comprando.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + comprando | I am buying |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + comprando | You were buying |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + comprando | He was buying |
| Future | Estar (future) + comprando | We will be buying |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + comprando | They would be buying |
Comprar Subjunctive Conjugations
Since it’s a regular verb, the subjunctive conjugations of comprar are formed by adding the corresponding subjunctive endings to the stem compr-. The subjunctive mood refers to wishes, suggestions, requests, and hypothetical situations.
Present subjunctive
The present subjunctive conjugations of comprar are used to talk about wishes, hopes, requests, and hypothetical situations. For example: tu mamá quiere que compremos más comida.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Compre | I buy |
| Tú | Compres | You buy |
| Él / Ella Usted | Compre | He/She buys You (formal) buy |
| Nosotros | Compremos | We buy |
| Vosotros | Compréis | You buy |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Compren | They buy You (plural) buy |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber in the present subjunctive + comprado is the structure you must use to build the present perfect subjunctive form of ‘comprar. For example, espero que Juan haya comprado más chocolates.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya comprado | I have bought |
| Tú | Hayas comprado | You have bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya comprado | He/She has bought You (formal) has bought |
| Nosotros | Hayamos comprado | We have bought |
| Vosotros | Hayáis comprado | You have bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan comprado | They have bought You (plural) have bought |
Imperfect subjunctive
The imperfect subjunctive of ‘comprar’ refers to past wishes, requests, or hypothetical situations. For example, si comprara este carro, me quedaría sin dinero.
In Spanish, the imperfect subjunctive has two conjugation models:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comprara | I bought |
| Tú | Compraras | You bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comprara | He/She bought You (formal) bought |
| Nosotros | Compráramos | We bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Compraran | They bought You (plural) bought |
Note: The table above doesn’t include the conjugation for vosotros because this pronoun is not used in Latin American Spanish.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comprase | I bought |
| Tú | Comprases | You bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comprase | He/She bought You (formal) bought |
| Nosotros | Comprásemos | We bought |
| Vosotros | Compraseis | You bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comprasen | They bought You (plural) bought |
Past perfect subjunctive
The past perfect subjunctive of ‘comprar’ talks about things you wish you bought or the hypothetical outcomes if you had bought something. For instance: ¡lo hubieras comprado!
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera comprado | I had bought |
| Tú | Hubieras comprado | You had bought |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera comprado | He/She had bought You (formal) had bought |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos comprado | We had bought |
| Vosotros | Hubierais comprado | You had bought |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran comprado | They had bought You (plural) had bought |
Comprar Imperative Conjugations
The imperative mood is used to give people instructions on what to do (affirmative commands) or not do (negative commands).
Affirmative commands
The affirmative imperative of ‘comprar’ is used to command people to buy something. For instance: compra dos litros de leche.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Compra | Buy |
| Usted | Compre | Buy |
| Vosotros | Comprad | Buy |
| Ustedes | Compren | Buy |
Negative commands
Notice that the negative imperative of ‘comprar’ uses the same conjugations as the present subjunctive. These negative commands can be used to order people not to buy something. Por favor, no compren más dulces.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No compres | Don’t buy |
| Usted | No compre | Don’t buy |
| Vosotros | No compréis | Don’t buy |
| Ustedes | No compren | Don’t buy |
Meanings of Comprar & Examples
Now that you’ve learned all the conjugations of comprar, check the following examples to see how to apply this verb into your conversations.
- Talking about purchases
¿Cuándo van a comprar los boletos?
When are you buying the tickets?
Espero que hayamos comprado suficiente comida.
I hope we have bought enough food.
Si sacan buenas calificaciones, les compraré un juguete.
If you guys have good grades, I’ll buy you a toy.
Take Note: Comprar is a common transitive verb. In other words, this verb can work with direct object pronouns (to talk about what you buy) and indirect object pronouns (to explain to or for whom you buy something).
- Referring to bribes
El equipo compró al árbitro.
The team bribed the referee.
Es obvio que el partido está comprado.
It’s obvious that the game is bought off.
Take Note: Some verbs in past participle form can also be used as adjectives. Those verbs work with estar to provide information about a person or object.
Download Comprar Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
I’ve created a PDF for you to download containing all of the conjugation tables, verb characteristics, and uses so you can study it at your own pace!
Practice Quiz: Comprar Conjugation

Put your skills to the test by taking our comprar quiz and practice conjugating this verb in all of the tenses listed above.





