As a regular verb, comer conjugation patterns can help you practice and learn how to conjugate -ER verbs in Spanish. Since this is also a basic verb for daily conversations, in this guide, we’ll go over:
- Comer Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Comer Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Comer Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Comer Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Comer Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Comer Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Comer
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -ER |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Comer |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Comiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Comido |
| Synonyms | Desayunar. |
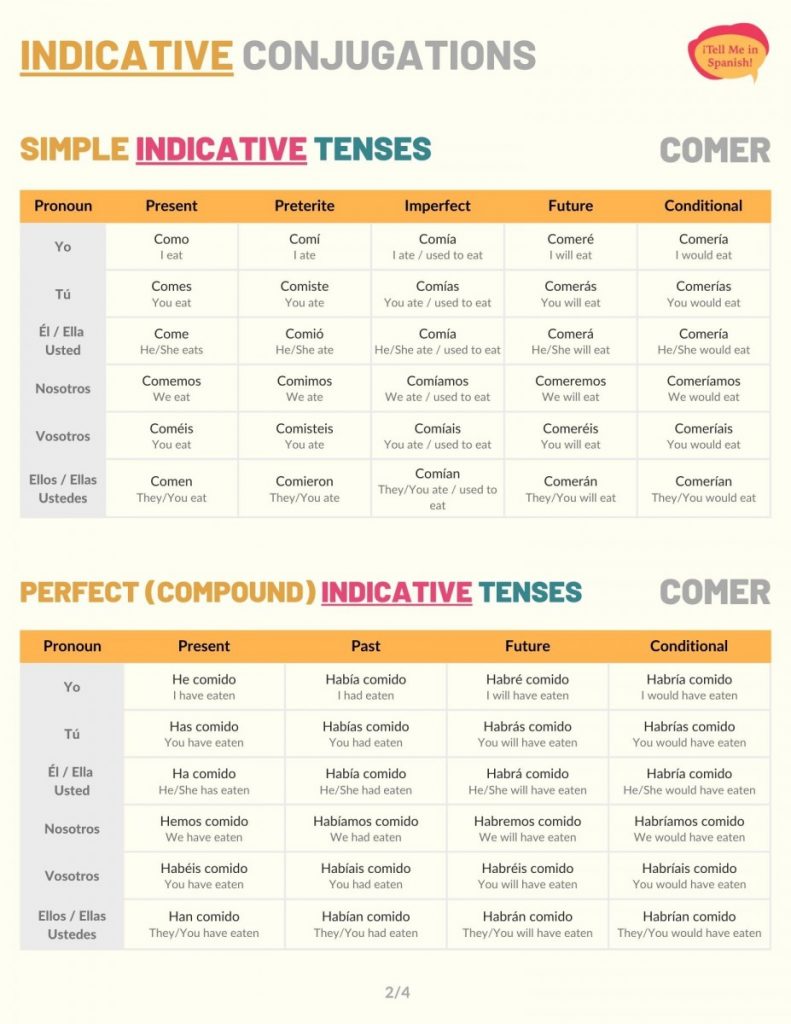
Indicative Conjugations of Comer
Present tense
Comer’s conjugation in the present tense is used to talk about what or when people habitually eat. For example: Yo no como mariscos.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Como | I eat |
| Tú | Comes | You eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Come | He/She eats You (formal) eat |
| Nosotros | Comemos | We eat |
| Vosotros | Coméis | You eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comen | They eat You (plural) eat |
Preterite tense
Comer preterite conjugations are regular. Use the preterite tense to express that a person ate something at a specific moment in the past. For instance: ¿Qué comieron ayer?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comí | I ate |
| Tú | Comiste | You ate |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comió | He/She ate You (formal) ate |
| Nosotros | Comimos | We ate |
| Vosotros | Comisteis | You ate |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comieron | They ate You (plural) ate |
Imperfect tense
Use comer imperfect conjugations to talk about what or when people used to eat something. You can include adverbs of manner to describe how someone ate. For example: Cuando era niño, mi hermano comía muy mal.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comía | I ate I used to eat |
| Tú | Comías | You ate You used to eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comía | He/She ate He/She used to eat You (formal) ate You (formal) used to eat |
| Nosotros | Comíamos | We ate We used to eat |
| Vosotros | Comíais | You ate You used to eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comían | They ate They used to eat You (plural) ate You (plural) used to eat |
Near future
The Spanish near or immediate future tense expresses that someone will eat at some point soon in the future. To form this tense, use ir in the present tense + a + comer. Here is an example: Hoy vamos a comer pollo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a comer | I’m going to eat |
| Tú | Vas a comer | You’re going to eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a comer | He/She is going to eat You (formal) are going to eat |
| Nosotros | Vamos a comer | We’re going to eat |
| Vosotros | Vais a comer | You’re going to eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a comer | They’re going to eat You (plural) are going to eat |
Future simple tense
Conjugate this verb to the future simple tense to express that a person will eat at some time in the future. For instance: ¿Qué comeremos en Navidad?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comeré | I will eat |
| Tú | Comerás | You will eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comerá | He/She will eat You (formal) will eat |
| Nosotros | Comeremos | We will eat |
| Vosotros | Comeréis | You (formal) will eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comerán | They will eat You (plural) will eat |
Conditional tense
The conditional indicative forms of this verb convey that a person would eat. If applicable to your statement, you can use si clauses to introduce the conditions that need to be fulfilled for this to happen. Nunca comería en ese lugar otra vez.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comería | I would eat |
| Tú | Comerías | You would eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comería | He/She would eat You (formal) would eat |
| Nosotros | Comeríamos | We would eat |
| Vosotros | Comeríais | You would eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comerían | They would eat You (plural) would eat |
Present perfect tense
Use haber present conjugations + the past participle of ‘comer’ to conjugate to the present perfect. These comer conjugations allow you to talk about what people have eaten. For example: ¿Qué es lo más extraño que han comido?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He comido | I have eaten |
| Tú | Has comido | You have eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha comido | He/She has eaten You (formal) have eaten |
| Nosotros | Hemos comido | We have eaten |
| Vosotros | Habéis comido | You have eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han comido | They have eaten You (plural) have eaten |
Past perfect
To say that someone had or hadn’t eaten something, conjugate this verb to the past perfect tense in Spanish. The formula to create this tense is haber in imperfect form + comido (past participle). Check this example: Gracias, no habíamos comido nada en todo el día.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había comido | I had eaten |
| Tú | Habías comido | You had eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había comido | He/She had eaten You (formal) had eaten |
| Nosotros | Habíamos comido | We had eaten |
| Vosotros | Habíais comido | You had eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían comido | They had eaten You (plural) had eaten |
Future perfect
When conjugated to the future perfect tense, comer conveys that a person will have eaten by or before a moment in the future. For instance: No sé qué habrás comido, pero no es lo que yo comí.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré comido | I will have eaten |
| Tú | Habrás comido | You will have eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá comido | He/She will have eaten You (formal) will have eaten |
| Nosotros | Habremos comido | We will have eaten |
| Vosotros | Habréis comido | You will have eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán comido | They will have eaten You (plural) will have eaten |
Conditional perfect
Conjugate comer to the conditional perfect tense to say that someone would have eaten something. For example: Habría comido más si no hubiera estado tan llena.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría comido | I would have eaten |
| Tú | Habrías comido | You would have eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría comido | He/She would have eaten You (formal) would have eaten |
| Nosotros | Habríamos comido | We would have eaten |
| Vosotros | Habríais comido | You would have eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían comido | They would have eaten You (plural) would have eaten |
Progressive tenses
In Spanish, the progressive tenses are formed with the conjugations of estar + present participle (comiendo for this verb). Use these comer conjugations to express that someone is eating at the moment of speaking. ¿Qué necesitas? Estamos comiendo.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + comiendo | I am eating |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + comiendo | You were eating |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + comiendo | He was eating |
| Future | Estar (future) + comiendo | We will be eating |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + comiendo | They would be eating |
Comer Subjunctive Conjugations
In Spanish, we must use the subjunctive mood to talk about a person’s demands, suggestions, desires, suggestions, uncertainty, or hypothetical outcomes. In the following sections, we’ll review comer conjugation charts for the most important subjunctive tenses.
Present subjunctive
Comer’s present subjunctive conjugations are applied to suggest, demand, or hope that someone eats something or in a certain way. Quiero que se coman toda la ensalada.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Coma | I eat |
| Tú | Comas | You eat |
| Él / Ella Usted | Coma | He/She eats You (formal) eat |
| Nosotros | Comamos | We eat |
| Vosotros | Comáis | You eat |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Coman | They eat You (plural) eat |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber’s present subjunctive forms + comido is how you form the present perfect subjunctive in Spanish. Use these comer conjugations to express hopes or uncertainty about whether someone has eaten something. No creo que mi hermano se haya comido tu hamburguesa.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya comido | I have eaten |
| Tú | Hayas comido | You have eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya comido | He/She has eaten You (formal) have eaten |
| Nosotros | Hayamos comido | We have eaten |
| Vosotros | Hayáis comido | You have eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan comido | They have eaten You (plural) have eaten |
Imperfect subjunctive
The imperfect subjunctive conjugations of comer allow you to talk about past suggestions, expectations, advice, or demands related to someone eating. For instance: El doctor me sugirió que comiera menos azúcar.
Castilian and Latin American Spanish use different endings for the imperfect subjunctive:
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comiera | I ate |
| Tú | Comieras | You ate |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comiera | He/She ate You (formal) ate |
| Nosotros | Comiéramos | We ate |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comieran | They ate You (plural) ate |
Note: Since the subject pronoun vosotros is not used in Latin American Spanish, the comer conjugation for this pronoun has not been included in the previous conjugation chart.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Comiese | I ate |
| Tú | Comieses | You ate |
| Él / Ella Usted | Comiese | He/She ate You (formal) ate |
| Nosotros | Comiésemos | We ate |
| Vosotros | Comieseis | You ate |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Comiesen | They ate You (plural) ate |
Past perfect subjunctive
Use comer’s past perfect subjunctive conjugations to say that someone would have eaten if a past circumstance had taken place. These forms can also be used to express regret for eating something or not. Si no hubiera estado aquí, ¿qué hubieran comido?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera comido | I had eaten |
| Tú | Hubieras comido | You had eaten |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera comido | He/She had eaten You (formal) had eaten |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos comido | We had eaten |
| Vosotros | Hubierais comido | You had eaten |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran comido | They had eaten You (plural) had eaten |
Comer Imperative Conjugations
To give commands to someone in Spanish, use the imperative mood.
Affirmative commands
If you need to order someone to eat, you must conjugate comer to the Spanish affirmative imperative. Cómete todas tus verduras.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Comas | Eat |
| Usted | Coma | Eat |
| Vosotros | Comed | Eat |
| Ustedes | Coman | Eat |
Negative commands
To order someone not to eat, use the negative command conjugations. Ya no comas más papas.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No comas | Don’t eat |
| Usted | No coma | Don’t eat |
| Vosotros | No comáis | Don’t eat |
| Ustedes | No coman | Don’t eat |
Meanings of Comer & Examples
Now that we’ve reviewed how to conjugate comer in Spanish, we’re about to learn how to use this verb correctly. Comer is used to talking about eating. However, we use pronouns in Spanish to add some nuances to this meaning:
[Comer conjugated] + [conjugated]
¿Era tuyo? Yo me lo comí.
Was it yours? I ate it.
Este cajero se come las tarjetas.
This ATM eats up the cards.
No eran ni las 2 y ya habíamos comido.
It wasn’t even 2, and we had already eaten.
Take Note: In its non-reflexive form, comer is only used to talk about eating habits or the time someone eats. However, we use pronominal pronouns to express that someone eats something entirely or to emphasize the amount of items a person eats. In this case, you can also add direct object pronouns to replace the thing someone ate (like example #1).
Download Comer Conjugation Charts & Uses Cheat sheet
Comer is one of the most common -ER verbs used in daily conversations, so it’s a key verb for learning Spanish. I’ve created a cheat sheet PDF containing all the comer conjugation charts as well as its definition and example sentences for you to review when you need to.
Practice Quiz: Comer Conjugation

Now that you’ve learned how to conjugate this regular -ER verb, the next step is to take the comer conjugation practice quiz. You can choose any combination of moods and tenses to include in the quiz, from beginner to advanced levels.





