Beber conjugation pattern can help you understand how to conjugate regular -ER verbs. Since this is also a common verb in everyday conversations, in this guide, we’ll go through the conjugation charts of beber. Here’s what you’ll learn:
- Beber Overview
- Indicative Tenses of Beber Conjugations
- Subjunctive Tenses of Beber Conjugations
- Imperative (Commands) of Beber Conjugations
- Uses & Examples
- Download Beber Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
- Beber Conjugation Practice Quiz
Overview of Beber
| Verb Characteristic | Property |
|---|---|
| Verb Type | -ER |
| Irregular | No |
| Infinitive | Beber |
| Gerund (Present Participle) Form | Bebiendo |
| Past Participle Form | Bebido |
| Synonyms | Tomar |
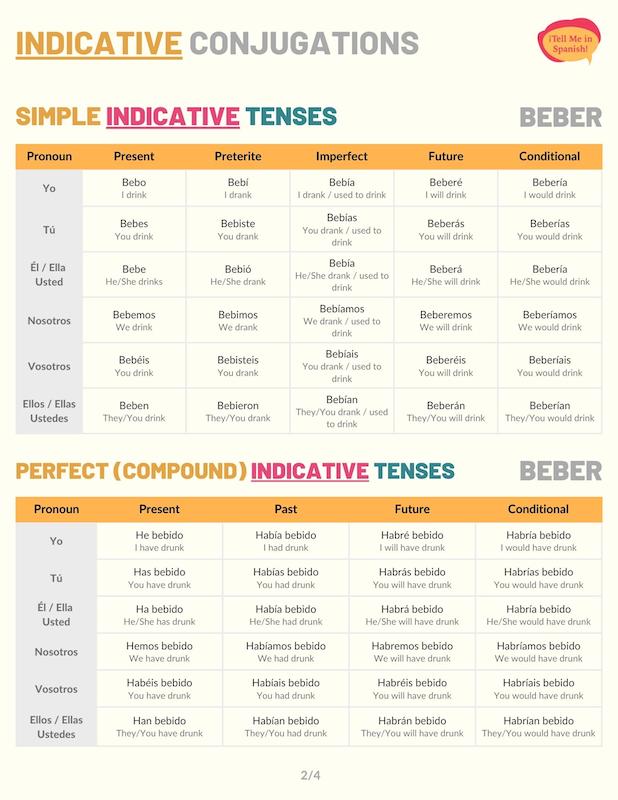
Indicative Conjugations of Beber
Present tense
Use the present tense conjugations of beber to ask or talk about what people usually drink. For example: Nunca bebo café antes de desayunar.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebo | I drink |
| Tú | Bebes | You drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebe | He/She drinks You (formal) drink |
| Nosotros | Bebemos | We drink |
| Vosotros | Bebéis | You drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Beben | They drink You (plural) drink |
Preterite tense
In the preterite tense, beber communicates that a person drank something at a specific time in the past. For instance: ¿Qué bebieron en la fiesta de Patty? As shown in the conjugation chart below, the preterite conjugations of ‘beber’ are regular.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebí | I drank |
| Tú | Bebiste | You drank |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebió | He/She drank You (formal) drank |
| Nosotros | Bebimos | We drank |
| Vosotros | Bebisteis | You drank |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Bebieron | They drank You (plural) drank |
Imperfect tense
Beber conjugated to the imperfect tense is used to talk about the things you used to drink repeatedly in the past. Mi mamá siempre bebía dos tazas de café.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebía | I drank I used to drink |
| Tú | Bebías | You drank You used to drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebía | He/She drank He/She used to drink You (formal) drank You (formal) used to drink |
| Nosotros | Bebíamos | We drank We used to drink |
| Vosotros | Bebíais | You drank You used to drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Bebían | They drank They used to drink You (plural) drank You (plural) used to drink |
Near future
Ir + a + infinitive (in this case, beber) is the formula to build the near future. In this tense, beber expresses that someone is going to drink something. For example: Yo no voy a beber hoy.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Voy a beber | I’m going to drink |
| Tú | Vas a beber | You’re going to drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Va a beber | He/She is going to drink You (formal) are going to drink |
| Nosotros | Vamos a beber | We’re going to drink |
| Vosotros | Vais a beber | You’re going to drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Van a beber | They’re going to drink You (plural) are going to drink |
Future simple tense
Use the future conjugations of ‘beber’ to convey that someone will drink something at some point in the future. Yo nunca beberé sake.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Beberé | I will drink |
| Tú | Beberás | You will drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Beberá | He/She will drink You (formal) will drink |
| Nosotros | Beberemos | We will drink |
| Vosotros | Beberéis | You (formal) will drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Beberán | They will drink You (plural) will drink |
Conditional tense
Beber conditional conjugations are used to talk about the beverages someone would drink. For instance: Nosotros jamás beberíamos tanto jugo de naranja.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebería | I would drink |
| Tú | Beberías | You would drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebería | He/She would drink You (formal) would drink |
| Nosotros | Beberíamos | We would drink |
| Vosotros | Beberíais | You would drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Beberían | They would drink You (plural) would drink |
Present perfect tense
Haber in the present tense + bebido (past participle) is the formula of the Spanish present perfect tense. These conjugations express that someone has or hasn’t drunk something. For instance: ¿Nunca has bebido sake?
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | He bebido | I have drunk |
| Tú | Has bebido | You have drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Ha bebido | He/She has drunk You (formal) have drunk |
| Nosotros | Hemos bebido | We have drunk |
| Vosotros | Habéis bebido | You have drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Han bebido | They have drunk You (plural) have drunk |
Past perfect
In the past perfect tense, ‘beber’ communicates that someone had or hadn’t drunk something before some other reference point in the past. A las ocho, ya se habían bebido todo el té. To form the past perfect, use the imperfect form of ‘haber’ and the past participle form of ‘beber’.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Había bebido | I had drunk |
| Tú | Habías bebido | You had drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Había bebido | He/She had drunk You (formal) had drunk |
| Nosotros | Habíamos bebido | We had drunk |
| Vosotros | Habíais bebido | You had drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habían bebido | They had drunk You (plural) had drunk |
Future perfect
The future perfect tense conjugations of ‘beber’ are used to say that someone will have drunk something by or before a certain point in the future. This tense also refers to drinks someone might have drunk. For instance: Para cuando llegues, ya habremos bebido nuestro café.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habré bebido | I will have drunk |
| Tú | Habrás bebido | You will have drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habrá bebido | He/She will have drunk You (formal) will have drunk |
| Nosotros | Habremos bebido | We will have drunk |
| Vosotros | Habréis bebido | You will have drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrán bebido | They will have drunk You (plural) will have drunk |
Conditional perfect
The conditional perfect conjugations of beber are used to talk about what someone would have drunk if certain conditions had been met. For instance: Habría bebido más, pero mañana tengo que trabajar.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Habría bebido | I would have drunk |
| Tú | Habrías bebido | You would have drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Habría bebido | He/She would have drunk You (formal) would have drunk |
| Nosotros | Habríamos bebido | We would have drunk |
| Vosotros | Habríais bebido | You would have drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Habrían bebido | They would have drunk You (plural) would have drunk |
Progressive tenses
The progressive tenses of beber convey that someone is drinking at the moment of speaking. Or, in the case of past forms (preterite and imperfect), to communicate that a past action was in progress when a person was drinking something. For example: ¿Qué están bebiendo?
Spanish progressive tenses are conjugated by using the formula estar conjugated + present participle of beber.
| Progressive Tense | Formula | Translation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Estar (present) + bebiendo | I am drinking |
| Preterite | Estar (preterite) + bebiendo | You were drinking |
| Imperfect | Estar (imperfect) + bebiendo | He was drinking |
| Future | Estar (future) + bebiendo | We will be drinking |
| Conditional | Estar (conditional) + bebiendo | They would be drinking |
Beber Subjunctive Conjugations
The Spanish subjunctive mood is used to describe wishes, discuss hypothetical situations or express uncertainty. The beber conjugation charts below show how to conjugate this verb to the subjunctive tenses.
Present subjunctive
The present subjunctive conjugations of beber are used to recommend, request or wish that someone drinks something. For example: Te sugiero que no bebas más café.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Beba | I drink |
| Tú | Bebas | You drink |
| Él / Ella Usted | Beba | He/She drinks You (formal) drink |
| Nosotros | Bebamos | We drink |
| Vosotros | Bebáis | You drink |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Beban | They drink You (plural) drink |
Present perfect subjunctive
Haber in the present subjunctive + bebido is the formula to build the present perfect subjunctive of ‘beber’. We use these conjugations to express doubt or expectations about someone having drunk something. Espero que se hayan bebido su jugo.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Haya bebido | I have drunk |
| Tú | Hayas bebido | You have drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Haya bebido | He/She has drunk You (formal) have drunk |
| Nosotros | Hayamos bebido | We have drunk |
| Vosotros | Hayáis bebido | You have drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hayan bebido | They have drunk You (plural) have drunk |
Imperfect subjunctive
Use the imperfect subjunctive conjugations of ‘beber’ to talk about past suggestions or expectations you had about someone drinking something. The wishes or expectations expressed by this tense are usually difficult to accomplish. Ojalá no bebieran tanto café.
The imperfect subjunctive has two models for conjugating ‘beber’ depending on which type of Spanish you’re using.
Latin American Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebiera | I drank |
| Tú | Bebieras | You drank |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebiera | He/She drank You (formal) drank |
| Nosotros | Bebiéramos | We drank |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Bebieran | They drank You (plural) drank |
Note: The conjugation chart above doesn’t include the form vosotros as this pronoun is not used in Latin American Spanish.
Castilian Spanish version
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Bebiese | I drank |
| Tú | Bebieses | You drank |
| Él / Ella Usted | Bebiese | He/She drank You (formal) drank |
| Nosotros | Bebiésemos | We drank |
| Vosotros | Bebieseis | You drank |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Bebiesen | They drank You (plural) drank |
Past perfect subjunctive
In the past perfect subjunctive, beber conveys that someone would have drunk something if a past circumstance was met. You can also use these conjugations to express regrets or hypothetical results if someone had drunk something.
For example: Ojalá no hubiéramos bebido tanto.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | Hubiera bebido | I had drunk |
| Tú | Hubieras bebido | You had drunk |
| Él / Ella Usted | Hubiera bebido | He/She had drunk You (formal) had drunk |
| Nosotros | Hubiéramos bebido | We had drunk |
| Vosotros | Hubierais bebido | You had drunk |
| Ellos / Ellas Ustedes | Hubieran bebido | They had drunk You (plural) had drunk |
Beber Imperative Conjugations
The Spanish imperative is used to order people to do (affirmative commands) or not do something (negative commands)
Affirmative commands
We use the affirmative imperative of ‘beber’ to order someone to drink something. For instance: Por favor, beba más agua. These conjugations are regular.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | Bebe | Drink |
| Usted | Beba | Drink |
| Vosotros | Bebed | Drink |
| Ustedes | Beban | Drink |
Negative commands
Use the negative imperative to demand someone to not drink something. For example: No beban agua de la llave.
| Person | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Tú | No bebas | Don’t drink |
| Usted | No beba | Don’t drink |
| Vosotros | No bebáis | Don’t drink |
| Ustedes | No beban | Don’t drink |
Meanings of Beber & Examples
Now that you’ve learned how to conjugate beber in Spanish, we’ll go over a few examples so you see how to apply this verb correctly.
[Beber conjugated] + beverage)
¿Cuántas cervezas han bebido?
How many beers have you guys drunk?
Matt siempre bebe su café sin azúcar.
Matt always drinks his coffee without sugar.
In Spanish, we use reflexive pronouns to emphasize the action of drinking. We do this when we want to highlight that someone drinks something or to stress the amount of beverages they have had.
[Reflexive pronoun] + [beber conjugated] + (beverage)
¿Quién se bebió mi coca?
Who drank my coke?
Tony y yo nos bebimos todo el vino.
Tony and I drank all the wine.
Take Note: In Latin American Spanish, tomar is more commonly used instead of ‘beber’ to say ‘to drink’.
Download Beber Conjugation Tables & Uses Cheat sheets
Download a copy of the ‘beber’ conjugation cheat sheets PDF with all the tense charts, meanings & uses.
Practice Quiz: Beber Conjugation

Take the beber conjugation practice quiz to test your knowledge of conjugating this -ER verb that is used in daily Spanish conversations.



