As a long-time Spanish teacher, I know how important it is to master the conjugation of -ar verbs in Spanish. Why? Because almost 83% of the verbs we use daily end with -ar.
Given that these are the most common verbs you’ll find, this guide will cover everything from conjugating -ar verbs, including their endings, to identifying the most essential -ar verbs necessary for conversational Spanish.
What Are & How to Conjugate -AR Verbs in Spanish
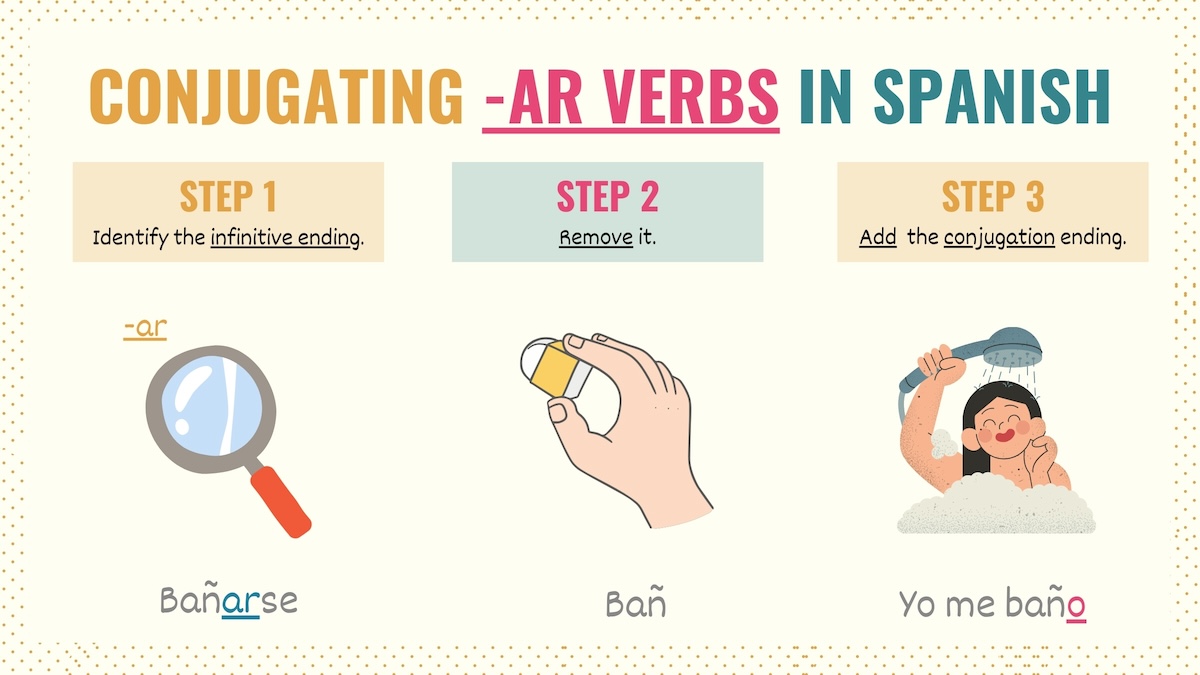
Spanish verbs are classified based on their infinitive ending. In other words, “-ar verb” simply refers to verbs ending in –ar, such as:
- Trabajar – To work
- Bañarse – To shower
- Necesitar – To need
This infinitive –ar ending determines the conjugation endings we must use for these verbs.
To conjugate both stem-changing and regular –ar verbs in Spanish, replace the infinitive ending with the appropriate conjugation ending for the subject and tense required. Note that irregular -ar verbs may require special endings.
Let’s take the Spanish present indicative tense as an example. The present endings for –ar verbs are:
- Yo: -o
- Tú: -as
- Él/Ella/Usted: -a
- Nosotros: -amos
- Vosotros -áis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes: -an
In table, you can see an example of how to conjugate –ar verbs in Spanish:
| Person | Necesitar | Cerrar |
| Yo | Necesito | Cierro |
| Tú | Necesitas | Cierras |
| Él / Ella / Usted | Necesita | Cierra |
| Nosotros | Necesitamos | Cierramos |
| Vosotros | Necesitáis | Cierráis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | Necesitan | Cierran |
Note that cerrar is an –ar stem-changing verb in the present tense. Despite its stem change, it still uses the regular -ar endings.
Take Note: Many students have difficulties conjugating Spanish reflexive verbs, such as ‘bañarse’. The ending se doesn’t affect the conjugating endings used. It only indicates that you must add a reflexive pronoun –me baño, te bañas, se baña, nos bañamos, se bañan.
In the conjugation chart below, you’ll find the endings to conjugate Spanish –ar verbs in the preterite, imperfect, conditional, and future tenses:
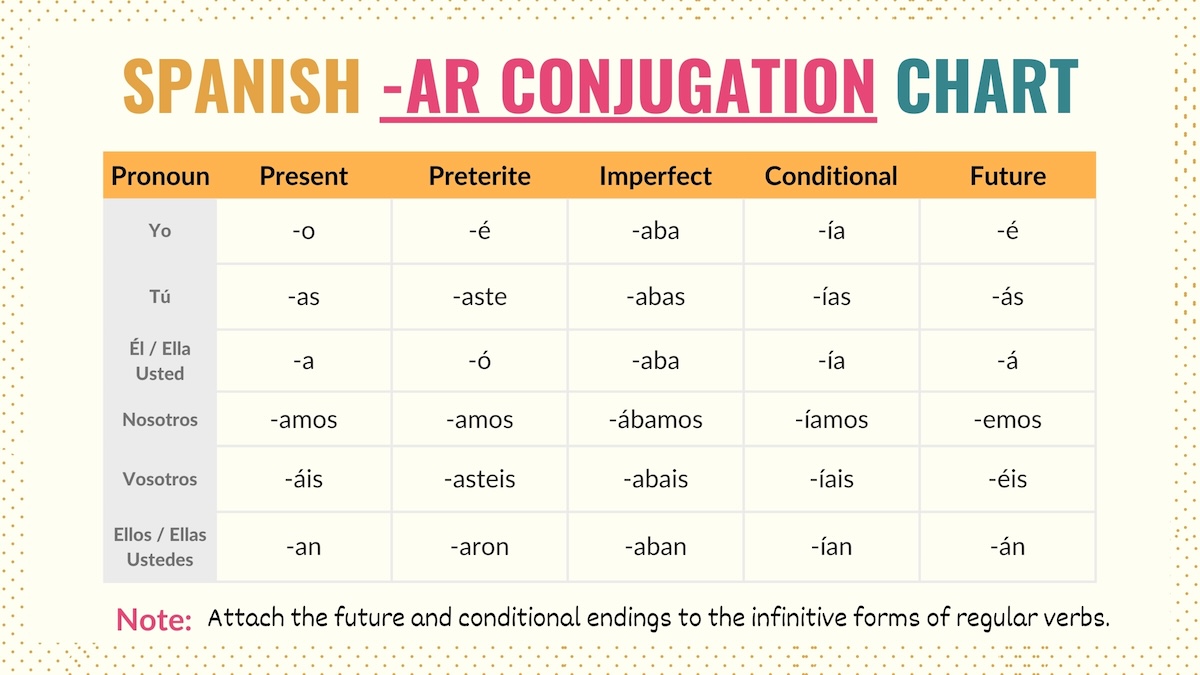
Take Note: The future simple and conditional tenses are formed by attaching the -ar endings to the infinitive verb. Me bañaré, te bañarás, se bañará, etc.
List of Most Common -Ar Verbs in Spanish
The following list contains the most important stem-changing and regular –ar verbs that you must know to improve your Spanish:
- Acabar: To finish
- Aceptar: To accept
- Acostarse: To lay down
- Afeitar: To shave
- Agarrar: To take/To capture
- Amar: To love
- Apagar: To turn off
- Arreglar: To fix / To get ready
- Avisar: To advise
- Ayudar: To help
- Bailar: To dance
- Bajar: To go down / To get out of
- Bañar: To bathe / To shower
- Borrar: To erase
- Buscar: To search
- Calentar: To heat up / To fire up
- Cambiar: To change / To exchange
- Caminar: To walk
- Cansar: To tire / To bore
- Cantar: To sing / To chirp
- Cenar: To eat dinner
- Cerrar: To close
- Cepillar: To brush
- Cocinar: To cook
- Comenzar: To start / To begin
- Comprar: To buy / To bribe
- Contar: To count / To tell
- Contestar: To answer / To talk back
- Continuar: To continue / To carry on
- Cortar: To cut / To break up
- Costar: To cust
- Cuidar: To take care / To keep an eye on
- Dejar: To leave / To stop doing something
- Desayunar: To have breakfast
- Descansar: To rest
- Desear: To wish
- Despertar: To wake up
- Duchar: To shower
- Empezar: To start / To begin
- Encontrar: To find
- Enseñar: To show / To teach
- Entender: To understand
- Entrar: To enter / To fit
- Enviar: To send
- Equivocarse: To be make a mistake / To be wrong
- Escuchar: To listen
- Esperar: To wait / To hope
- Estudiar: To study / To look into
- Explicar: To explain
- Funcionar: To work / To run
- Ganar: To win / To earn
- Gastar: To spend / To use
- Guardar: To keep / To put away
- Gustar: To like
- Hablar: To speak / To call
- Intentar: To try
- Interesar: To interest
- Invitar: To invite / To treat
- Jugar: To play
- Lavar: To wash
- Levantarse: To lift / To wake up
- Limpiar: To clean
- Llamar: To call / To name
- Llegar: To arrive
- Llevar: To take / To have been
- Mandar: To send / To order
- Manejar: To manage / To drive
- Mejorar: To improve
- Mirar: To look
- Molestar: To bother / To be upset
- Necesitar: To need
- Olvidar: To forget
- Ordenar: To order / To tidy up
- Pagar: To pay
- Parar: To stop / To stand up
- Pasar: To pass / To happen
- Peinar: To comb
- Pensar: To think / To believe
- Perdonar: To forgive
- Practicar: To practice
- Preguntar: To ask / To wonder
- Preocupar: To worry / To care
- Preparar: To prepare
- Probar: To try / To taste
- Quedar: To stay / To be left
- Quitar: To take off / To get out of the way
- Recordar: To remember
- Regresar: To return
- Rentar: To rent
- Sacar: To take out
- Secar: To dry
- Sentarse: To sit
- Terminar: To finish / To break up
- Tirar: To throw / To throw away
- Tocar: To play / To touch
- Tomar: To take / To drink
- Trabajar: To work
- Usar: To use / To wear
- Viajar: To travel
- Visitar: To visit
Irregular -ar verbs
There are three irregular –ar verbs in Spanish that you should master:
Keep in mind that these verbs may be irregular only in certain tenses. Check out the conjugation charts below to spot the irregular conjugations.
Estar:
| Person | Present | Preterite |
| Yo | Estoy | Estuve |
| Tú | Estás | Estuviste |
| Él / Ella / Usted | Está | Estuvo |
| Nosotros | Estamos | Estuvimos |
| Vosotros | Estáis | Estuvisteis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | Están | Estuvieron |
Dar:
| Person | Present | Preterite |
| Yo | Doy | Di |
| Tú | Das | Diste |
| Él / Ella / Usted | Da | Dio |
| Nosotros | Damos | Dimos |
| Vosotros | Dais | Disteis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | Dan | Dieron |
Take Note: In the present tense, estar and dar are highly irregular for the pronoun ‘yo’. For the other subject pronouns, we add or remove accent marks for spelling reasons.
Finally, andar is only irregular in the preterite tense, where it follows a similar conjugation pattern to estar. Be aware that in everyday situations, andar is often used as an informal synonym for estar.
Andar:
| Person | Preterite |
| Yo | Anduve |
| Tú | Anduviste |
| Él / Ella / Usted | Anduvo |
| Nosotros | Anduvimos |
| Vosotros | Anduvisteis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | Anduviero |
Beyond -Ar Verbs in Spanish
As mentioned at the beginning of this guide, most of the verbs we use in our everyday conversations are –ar verbs. However, there are also key Spanish –er and -ir verbs that you need to master to communicate effectively.
Make sure you know how to conjugate –ar verbs across different Spanish tenses, so you can start applying them into your conversations. Click the button below to download the cheat sheets for this lesson:



