I’ve had students who were able to understand, speak, and hold conversations beautifully in Spanish. However, when it comes to the “simple” stuff, such as saying dates in Spanish, they start to struggle. There is no shame in this! The Spanish formatting for saying or writing dates can throw you off if you’re unfamiliar with it.
So, in this guide, I’ll teach you the key elements and formulas you need to write or say dates in Spanish. Here are the things we’ll go over:
Dates are a frequent element in our conversations. Some common applications are setting appointments, saying someone’s birthday, or creating time markers for the preterite tense.
How to Write the Date in Spanish
Whether you want to say or write the date in Spanish, you need to use the following elements:
- Days in Spanish
- Lunes – Monday
- Martes – Tuesday
- Miércoles – Wednesday
- Jueves – Thursday
- Viernes – Friday
- Sábado – Saturday
- Domingo – Sunday
- Months
- Enero – January
- Febrero – February
- Marzo – March
- Abril – April
- Mayo – May
- Junio – June
- Julio – July
- Agosto – August
- Septiembre – September
- Octubre – October
- Noviembre – November
- Diciembre – December
- Masculine definite article ‘el’
- Numbers in Spanish
- From 1 to 31 to indicate the day of the month
- Large numbers to say the year
- Preposition ‘de’
While there are several formats you can use to say or write the date in Spanish (covered below), the order of primary elements for dates is always the same:
1. Day
2. Month
3. Year
As you can see, in Spanish, the day and the month have the inverse order than English. With this in mind, let’s jump to see some formulas and examples.
Take Note: Date is called ‘fecha’ in Spanish. Although in English the word ‘date’ is used in many contexts, idioms, and expressions, the word fecha is not always used in those situations.
Siempre trato de mantenerme al día.
I always try to be up to date.
Becky y Josh tuvieron una cita doble.
Beck and Josh had a double date.
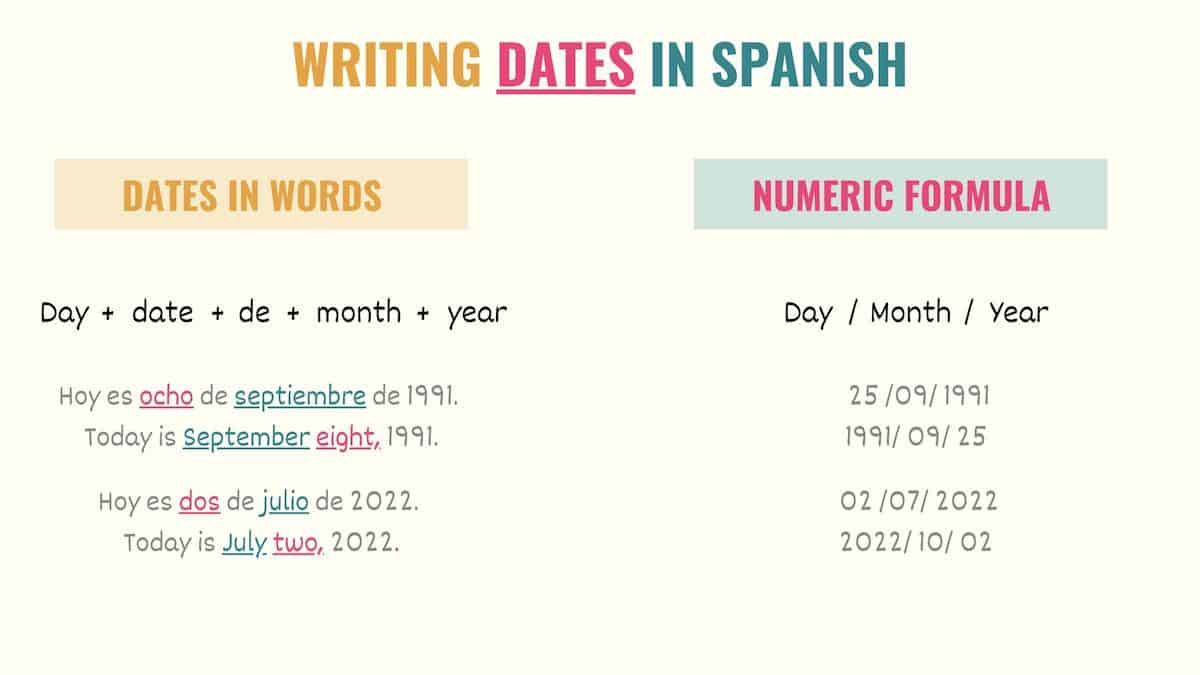
Numeric format for writing dates
Below is the numeric format for dates in Spanish along with some examples:
[Day] / [month] / [year]
08/08/1992
14/02/2010
25/01/07
Tip: you can write down the last two digits of the year to abbreviate your date.
Formatting for writing dates in Spanish
If instead you need to write the full date with words, you can use the formula below. Notice that you can omit some elements depending on how precise you need your date to be:
[Day of the week] + [date] + de + [month] + de + [year]
Me voy el lunes 25 de septiembre.
I’m leaving on Monday, September 25.
Hoy es ocho de agosto de 2022.
Today is August 8th, 2022.
La fecha de caducidad es el diez de enero de dos mil veinte.
The expiration date is January tenth two thousand twenty.
Tu hija nació el 20 de noviembre de 1991.
Your daughter was born on the 20th of November, 1991.
If some of the examples look strange in English, it’s because I’m illustrating how it’s common to mix numbers and words when writing dates in Spanish. In very few formal circumstances, you may be required to write the full date with words. Doing so requires you to be very familiar with numbers in Spanish.
In the sections below, I’ll teach you what verbs to use when giving the date. But first, let’s address several common questions you may have about using dates in Spanish.
Are dates in Spanish capitalized?
Dates in Spanish are never capitalized unless they are used to start a sentence. Since ‘el’ is usually the first element of the date, it would need to be capitalized in this situation. If the date is in the middle of a sentence, none of its elements should be capitalized.
Look at the two examples below, one where the sentence starts with the date, and therefore “el” is capitalized and the other where the sentence doesn’t start with the date.
El 20 de mayo regresé a México.
I came back to Mexico on May 20th.
Regresé a México el 20 de mayo.
I came back to Mexico on May 20th.
Are dates in Spanish masculine or feminine?
Dates in Spanish are masculine since they are built with months and numbers (for days and years), which are all masculine words. Because of this, when using days of the week to say the date, you must include the masculine definite article.
Giving the Dates in Spanish
When saying dates in Spanish, we use the verb ser when referring to appointments or giving the date.
Remember that, based on the information you need to convey, you can add or omit certain elements of this formula.
[‘Ser’ conjugated] + el + (day of the week) + [date] + de + [month]
Su cita es el lunes 20 de agosto.
Your appointment is on Monday, August 20.
Hoy es 15 de julio.
Today is July 15.
Tu cita fue el 30 de enero.
Your appointment was on January 30.
Conversational tip: you can also use the more informal expression estamos a + date to tell today’s date.
Hoy estamos a 10 de marzo.
Today’s date is March 10.
If you want to say the date when an event takes place, you need to use different verbs. These events can be anything from birthdays, holidays, anniversaries to expiration dates. Check these examples:
[Verb conjugated] + el + (day of the week) + [date] + de + [month]
Judith nació el 2 de julio de 1970.
Judith was born on July 2, 1970.
La leche se vence el siete de abril.
The milk expires on April seventh.
Cristóbal Colón descubrió América el 12 de octubre de 1492.
Christopher Columbus discovered America on October 12, 1492.
Questions to Ask the Date
Now that you know how to say the date in Spanish, here are some common questions you can use to ask others for the date:
- ¿Cuál es la fecha? – What’s the date?
- ¿A qué estamos hoy? – What’s today’s date?
- ¿Qué día es hoy? – What day is today?
- ¿Cuál es la fecha de hoy? – What’s today’s date?
If you use the question ¿qué día es hoy?, don’t be surprised if some people just answer you by saying the day of the week.
Key Points
Knowing how to say dates in Spanish can help you avoid misunderstandings and improve your communication. When it comes to this topic, remember that:
- The correct order to write or say dates is day, month, and year.
- Spanish dates are only capitalized if they are at the beginning of a sentence.
- Dates in Spanish are masculine and use the definite article ‘el’.
- The verb ‘ser’ is only used to talk about appointments or give the date.