As one of the nine parts of speech, Spanish nouns are crucial in helping us communicate and express our thoughts. So, on this page, we’ll explore what nouns are, why they’re essential, and how they work. I’ll also provide links to useful resources to help you learn more about specific aspects of nouns.
What Are Nouns in Spanish?
A noun in Spanish is a word that names, labels, or represents people, places, things, or ideas. They’re one of the building blocks of the Spanish language. In other words, a sentence is incomplete without a noun.

Depending on their characteristics, nouns can be classified as either proper and common. A proper noun is a name we use to identify specific places or people. For example:
María vive en Colombia.
María lives in Colombia.
On the other hand, a common noun refers to people, places, animals, things, and concepts in general. For instance:
El libro que está en la mesa es mío.
The book on the table is mine.
Types of Nouns
These types of Spanish nouns have different sub-classifications. So, based on how they’re formed and the information they deliver, these nouns can be:
- Concrete nouns: refer to material things you can perceive.
- Abstract nouns: represent concepts, feelings or ideas.
- Uncountable nouns: talk about things that you cannot count with exact amounts.
- Countable nouns: refer to objects that can be quantified with numbers or precise amounts.
- Collective nouns: are nouns that refer to a group of people or things.
- Individual nouns: a noun that talks about a single thing. It can have a plural form.
- Simple nouns: are nouns formed by one word.
- Compound nouns: are words formed with two terms.
In the additional resources below, you’ll find a guide to types of nouns where you can learn how each category works. Additionally, you’ll find a list of basic nouns you should include to your Spanish vocabulary.
Take Note: In Spanish, los sustantivos (nouns) have gender. Simply put, these words can be masculine (like ‘carro’) or feminine (like ‘silla’) and have singular or plural forms.
How and When to Use a Noun in Spanish?
A Spanish noun can be used as the:
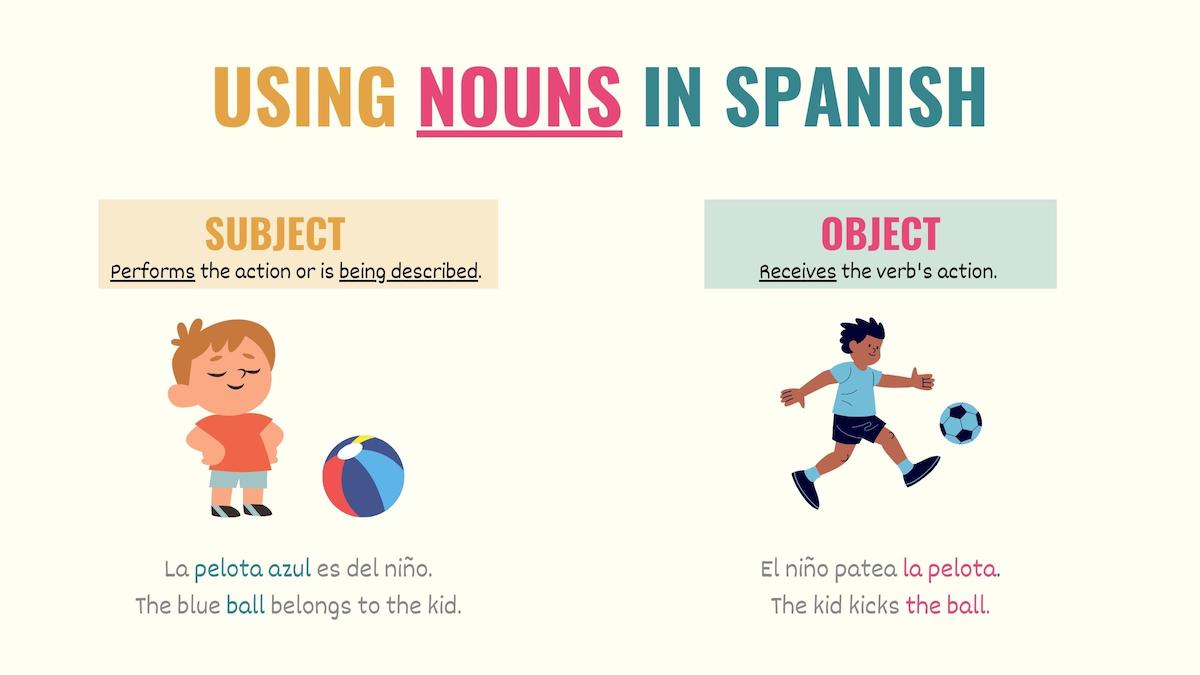
1. Subject of a sentence to explain who performs the action or how something is.
La manzana es roja.
The apple is red.
Ben habla español.
Ben speaks Spanish.
Take Note: When working as the subject of a sentence, a noun can be replaced with its corresponding subject pronoun.
2. Object of a sentence to indicate that something or someone receives or is affected by the action.
Yo me comí la manzana.
I ate the apple.
Mis vecinos le hablaron a Ben.
My neighbors called Ben.
Take Note: In Spanish, if the noun receives the verb’s action (like example #1), it’s working as a direct object. However, a noun affected by or benefited from the action is an indirect object (like example 3).
Although English nouns are used in possessive forms, in Spanish, nouns cannot be used like this:
La pelota de mi perro es roja.
My dog’s ball is red.
Rules for Spanish Nouns

Here are the essential rules you must know to use these Spanish words correctly:
- Gender: Nouns in Spanish have a gender. Masculine nouns refer to males and things that are grammatically masculine. Mostly, words ending with an ‘o’ are masculine words. On the other hand, Spanish feminine nouns are used to talk about women or female objects. Most of the time, a noun ending with an ‘a’ is likely feminine. However, there are numerous other endings and some exceptions to these rules.
- Plural forms: In Spanish, the plural form refers to a group of things or people. A noun is often changed from singular to plural by adding an ‘s’. However, there are some spelling changes and considerations you need to keep in mind (such as how to mark the number if a word naturally ends in ‘s’).
- Agreement: One of the basic rules of Spanish grammar is that adjectives and determiners must agree in number and, sometimes, in gender with nouns. For instance, when working with feminine nouns you must ensure that the words modifying that noun also convey this information.
- Determiners: In Spanish, nouns are always accompanied by a determiner. Choosing these types of words depends on what you need to express (possession, specificity, proximity, etc).
- Capitalization: Depending on the noun type, you must follow different Spanish capitalization rules. For example, proper nouns must always be capitalized, whereas common nouns are only capitalized if they start the sentence.
Top Spanish Resources for Nouns
Now that you have a basic understanding of nouns, here are some Spanish topics you should check:
- List of Common Nouns: Increase your Spanish vocabulary with this list of nouns. It includes feminine, masculine, uncountable, and other types of nouns, along with their respective translations.
- Types of Nouns: Nouns actually have many different classifications, which dictate many of their rules. Check this quick section to learn these different types which will help you identify when certain nouns are masculine, feminine, singular, plural as well as how to use them correctly.
- Nouns and Articles: A noun is often preceded by a Spanish article. Since these words are so commonly used together, in this resource, you’ll find how to use them together.
- Guide to Diminutives: Diminutives are very common in conversational Spanish. As a result, this resource is meant to teach you the endings to form these words as well as when and how to use them.
- Gender of Nouns: As established before, nouns can be feminine or masculine in Spanish. Since gender is crucial for effective communication, this resource contains the information you need to identify feminine and masculine nouns.
- Guide to Plural Words: Check this guide if you’re wondering how to transform a word from singular to the plural form.
- Capitalization Rules: Nouns in English do not always work the same way as in Spanish. One of the main differences between these languages is their capitalization rules for nouns. Find out more about when to use upper and lowercase letters in Spanish.
Additional Resources for Nouns
If you’re ready to take nouns to the next level, here are some additional resources you can explore:
- Spanish Pronouns: As long as the context is clear, in Spanish, nouns can be replaced to shorten the sentence and avoid repetition. Depending on the role of the noun, you may need to use a subject or an object pronoun.
- Determiner Words: Nouns rarely work on their own. In fact, most of the time, these words are preceded by a determiner. These words allow you to convey specific information about a noun. El, la, un, una are examples of determiners. This resource will provide you with a list of determiners and their characteristics.
- Spanish Adjectives: Adjectives describe and modify nouns. In other words, they help you understand a noun’s qualities. For example, if you wanted to say how a person is, you would need to use adjectives to describe people. Remember that, these words are subject to agreement (they can be singular, plural, feminine or masculine).
- Parts of Speech: Nouns are one of the parts of speech. These types of words are essential to forming sentences. In this guide, I’ll explain what these Spanish words are and how they work.
Download the Spanish Guide to Nouns PDF Cheat Sheet
There are many different nouns in Spanish you need to learn to become conversational or fluent. They also have many rules, including their gender (masculine vs feminine), types (common, proper, etc.), and other parts of speech which you must use in conjunction with nouns.



